What are the Isotopes, Isobars and Isotones of an Element
- The proton number of an atom determines the type of element. For example, the proton number Z = 11 is for the element sodium while Z = 12 is for magnesium.
Therefore, all atoms of the same element contain the same number of protons. - The number of neutrons in the atoms of an element may be different. These atoms have different nucleon numbers
- Most sodium atoms have 12 neutrons in their nucleus. Some sodium atoms have 13 neutrons.
- Table gives the summary of the compositions and notations of these two atoms of sodium.
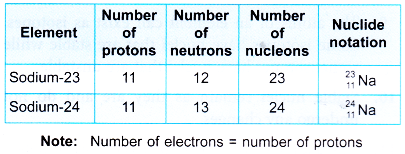
- Sodium-23 and sodium-24 are known as isotopes of sodium.
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of an element which have the same proton number but different nucleon numbers.
Example: Hydrogen is the common example which has three isotopes. These have the same atomic number, one, but different mass numbers 1, 2, and 3. These three isotopes are commonly known as hydrogen or protium, deuterium (D) and tritium (T) respectively. Since atomic number is same for all the three, they all have one electron and therefore, one proton but different neutrons.
(1) Hydrogen At. No. = 1, Mass no. = 1
Electrons = 1, Protons = 1, Neutrons = 0
It is also represented as \(_{ 1 }^{ 1 }{ H }\)
(ii) Deuterium At. No = 1, Mass no. = 2
Electron = 1, Protons = 1, Neutrons = 1
It is also represented as \(_{ 1 }^{ 2 }{ H }\) or D
(iii) Tritium At. No = 1, Mass no. = 3
Electron = 1, Protons = 1, Neutrons = 2
It is also represented as \(_{ 1 }^{ 3 }{ H }\) or T.
Isotopes of Hydrogen
Protium | Deuterium | Tritium | |
| Atomic number, Z | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Mass number, A | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Number of protons | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Number of electrons | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Number of neutrons | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Electronic configuration | K 1 | K 1 | K 1 |
People also ask
- What is the Radioactive Isotope?
- Radioactivity: Types of Radioactive Emissions
- How do you detect radioactivity?
- What is nucleus of an atom?
- What is the half life of a radioactive element?
- What are the different types of radioactive decay?
- Importance of Proper Management of Radioactive Substances
- How would you describe the Structure of an Atom
- What was Rutherford’s Original Hypothesis
- What did Bohr Contribute to the Theory of an Atom
- What are the Characteristics of Electron, Proton and Neutron
- Explain Bohr Bury rules for Distribution of Electrons into Different Shells
- What did Dalton Contribute to the Understanding of the Atom
- What is the Definition of Atom and Molecule
- What is Atomic Mass
- How has the Model of the Atom Changed Over the Years?
Isotopes of Some Elements
| Element | Isotopes | Proton number | Nucleon number | Number of protons | Number of electrons | Number of neutrons |
| Hydrogen | Hydrogen-1 (\(_{ 1 }^{ 1 }{ H }\)) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Hydrogen-2 (\(_{ 1 }^{ 2 }{ H }\)) | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Hydrogen-3 (\(_{ 1 }^{ 3 }{ H }\)) | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Oxygen
| Oxygen-16 (\(_{ 8 }^{ 16 }{ O }\)) | 8 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Oxygen-17 (\(_{ 8 }^{ 17 }{ O }\)) | 8 | 17 | 8 | 8 | 9 | |
| Oxygen-18 (\(_{ 8 }^{ 18 }{ O }\)) | 8 | 18 | 8 | 8 | 10 | |
Carbon | Carbon-12 (\(_{ 6 }^{ 12 }{ C }\)) | 6 | 12 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Carbon-13 (\(_{ 6 }^{ 13 }{ C }\)) | 6 | 13 | 6 | 6 | 7 | |
| Carbon-14 (\(_{ 6 }^{ 14 }{ C }\)) | 6 | 14 | 6 | 6 | 8 | |
| Chlorine
| Chlorine-35 (\(_{ 17 }^{ 35 }{ Cl }\)) | 17 | 35 | 17 | 17 | 18 |
| Chlorine-37 (\(_{ 17 }^{ 37 }{ Cl }\)) | 17 | 37 | 17 | 17 | 20 | |
| Bromine
| Bromine-79 (\(_{ 35 }^{ 79 }{ Br }\)) | 35 | 79 | 35 | 35 | 44 |
| Bromine-81 (\(_{ 35 }^{ 81 }{ Br }\)) | 35 | 81 | 35 | 35 | 46 |
Some important points regarding isotopes:
- Isotopes of an element have the same
(a) proton number.
(b) number of protons in an atom.
(c) number of electrons in an atom.
(d) electron arrangement.
(e) chemical properties because they have the same electron arrangement. - Isotopes of an element have different
(a) nucleon numbers.
(b) numbers of neutrons in an atom.
(c) physical properties such as density, melting point and boiling point. However, these differences are very small.
Uses of isotopes in Medicine
- Gamma-rays emitted from cobalt-60 are used in radiotherapy for the treatment of cancer.
- Superficial cancers such as skin cancer can be treated by less penetrating radiation from phosphorus-32 or strontium-90.
- A heart pacemaker which contains plutonium-238 is used to regulate the heartbeats of patients with heart problems.
- Iodine-131 is used in the treatment of thyroid diseases.
- Carbon-14 can be used to estimate the age of bones, wood or fossils by measuring the fraction of carbon-14 it contains.
Uses of isotopes in Agriculture
- The uptake of phosphate and the metabolism of phosphorus by plants can be studied using a phosphate fertilizer containing phosphorus-32.
- Radioactive tracer studies using carbon -14 have helped in the understanding of photosynthesis and protein synthesis.
Uses of isotopes in Industry
- Sodium-24 can be used to trace leaks in gas or oil pipes and ventilating systems.
- Gamma rays of cobalt-60 are passed through food to destroy bacteria which cause the food to spoil without changing the quality, flavour or texture of the food.
- Radiation from krypton-85 can be used to control the thickness of plastic sheets in the industry.
Isobars
Isobars are the atoms of different elements having same mass number but different atomic numbers.
Since isobars have the same mass number, therefore sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of each is the same. These atoms differ in their atomic number and therefore, they have different number of protons and also different number of neutrons. Due to different atomic numbers, the isobars will have different atomic structures and therefore, will differ in chemical properties.
Example: Argon (atomic number 18) and calcium (atomic number 20) are isobars because they have same mass number 40.
| Argon (\(_{ 18 }^{ 20 }{ Ar }\)) | Calcium (\(_{ 20 }^{ 40 }{ Ca }\)) |
| At. no. = 18 | At. no. = 20 |
| Mass no. = 20 | Mass no. = 40 |
| No. of electrons = 18 | No. of electrons = 20 |
| No. of protons = 18 | No. of protons = 20 |
| No. of neutrons = 22 | No. of neutrons = 20 |
Isotones
- The atoms having same number of Neutrons but diffrent mass number are called Isotones.
- The atoms have different number of protons of atomic number.
- The isotones belong to two of more different elements.
- “(A–Z) is same” “A & Z are different”.
