How can we measure the strength of acids and alkalis?
- An acid produces hydrogen ions in aqueous solution. The acidity of a solution is a measure of the concentration of the hydrogen ions in the solution.
- A base produces hydroxide ions in aqueous solution. The alkalinity of a solution is a measure of the concentration of the hydroxide ions in the solution.
- In 1909, Soren Sorensen proposed the pH scale for measuring acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution.
The pH scale
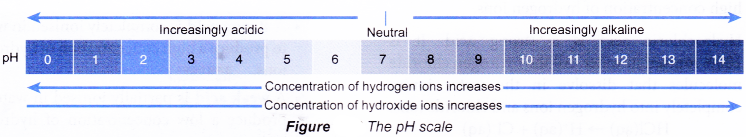
- The pH scale normally has a range of values from 0 to 14 to indicate how acidic or alkaline an aqueous solution is.
- The pH value measures the concentration of hydrogen ions or hydroxide ions.
pH < 7 → acidi solution
pH = 7 → neutral solution
pH > 7 → alkaline solution - The lower the pH value, the higher the concentration of hydrogen ions.
The higher the pH value, the higher the concentration of hydroxide ions. - The pH of values some common solutions used in daily life are shown below.
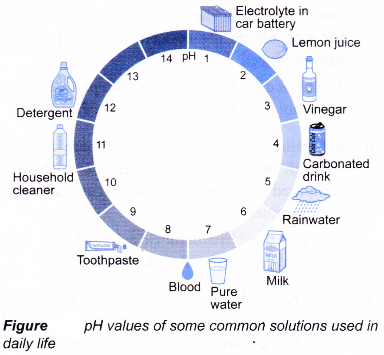
- The pH value of an aqueous solution can be measured by using
(a) Universal Indicator
(b) pH meter
(c) acid-base indicators

Table shows examples of acid-base indicators.
| Indicator | pH range | Colour change | ||
| Acid Neutral | Alkali | |||
| Methyl orange | 3.0 – 5.0 | Red | Orange | Yellow |
| Bromothymol blue | 6.0 – 8.0 | Yellow | Green | Blue |
| Phenolphthalein | 8.0-10.0 | Colourless | Colourless | Pink |
People also ask
- What is the definition of an acid and a base?
- What is the definition of an acid in chemistry?
- What is the definition of a base in chemistry?
- Classification of Acids
- Preparation of Acids
- What are the chemical properties of an acid?
- General Properties of Acids
- Uses of Acids
- Preparation of Bases
- General Properties of Bases
- What determines a Strong Base and a Weak Base
- What are the uses of Bases
- How to calculate concentration of acids and alkalis?
- How do you prepare a standard solution?
- What is meant by a neutralization reaction?
- How does titration determine concentration?
- Relationship between pH values and molarity of acids and alkalis
- Concept of the pH Scale
- Role of pH in everyday life
- What is the pH of a salt solution
Strong and weak acids
- The strength of an acid or alkali depends on the degree of dissociation of the acid or alkali in water.
- The degree of dissociation measures the percentage of acid molecules that ionise when dissolved in water.
- A strong acid is an acid which ionises or dissociates completely in water to produce a high concentration of hydrogen ions.
- Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid. It is 100% ionised in water. All the hydrogen chloride molecules that dissolve in the water ionise completely into hydrogen ions and chloride ions.
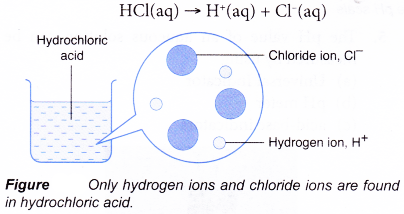
- A weak acid is an acid which ionises partially in water to produce a low concentration of hydrogen ions.
- Ethanoic acid is a weak acid. Dilute ethanoic acid is about 0.4% ionised, only 4 out of every 1000 ethanoic acid molecules ionise. As fast as the acid molecules ionise to produce ions, the ions combine back again to give the original acid molecules in a reversible reaction.
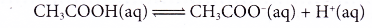
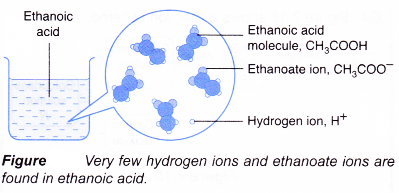
- Examples of strong and weak acids are shown in Table.
Acid Name Particles Strong acid Hydrochloric acid, HCl H+, Cl– Nitric acid, HNO3 H+, NO3– Sulphuric acid, H2S04 H+, HSO4–, SO42- Weak acid Carbonic acid, H2C03 H+, HCO3–, CO32-, H2CO3 Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH H+, CH3COO–, CH3COOH Sulphurous acid, H2SO3 H+, HSO3–, SO32-, H2SO3 - Strong acid and weak acid are defined as follows.
A strong acid is completely ionised in water to produce a high concentration of hydrogen ions.
A weak acid is partially ionised in water to produce a low concentration of hydrogen ions. - The pH of an acid solution changes with concentration of the acid. The concentration of the acid affects the concentration of hydrogen ions produced. For example:
10 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid: pH = 1
01 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid: pH = 2 - pH values can be used to compare the acid strength of different acids. All the acids to be compared must be of the same concentration.
For example:
10 mol dm-3hydrochloric acid: pH = 1
10 mol dm-3 ethanoic acid: pH = 3 - For two different acids of the same concentration, the acid with the lower pH value is the stronger acid, i.e. higher degree of ionisation in water.
Strong and weak alkalis
- Sodium hydroxide is a strong alkali. It ionises fully when dissolved in water.
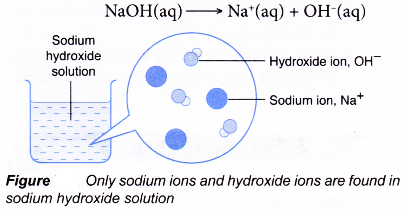
- A strong alkali is an alkali which is fully ionised in water to produce a high concentration of hydroxide ions.
- A weak alkali is an alkali which ionises partially in water to produce a low concentration of hydroxide ions.
- Ammonia is an example of a weak alkali. It is only partly ionised in water, which means the ionisation of ammonia in water is incomplete. Only a small amount of ammonia molecules are ionised in water to produce ammonium ions and hydroxide ions.
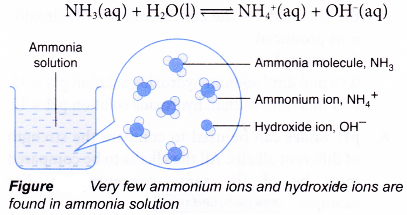
- Examples of strong and weak alkalis are shown in Table.
Alkali Name Particles Strong alkali Sodium hydroxide, NaOH Na+, OH– Potassium hydroxide, KOH K+, OH– Barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)2 Ba2+, OH– Weak alkali Ammonia, NH3 NH3, NH4+, OH– Methylamine, CH3NH2 CH3NH2, CH3NH3+, OH– Hydrazine, N2H4 N2H4, N2H5+, OH– - Strong alkali and weak alkali are defined as follows.
A strong alkali is completely ionised in water to produce a high concentration of hydroxide ions.
A weak alkali is partially ionisesed in water to produce a low concentration of hydroxide ions. - The pH of an alkali solution changes with concentration of the alkali. The concentration of the alkali affects the concentration of hydroxide ions produced.
For example:
10 mol dm-3m-3 sodium hydroxide solution pH = 13
01 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide solution pH = 12 - pH values can be used to compare the strength of different alkalis. All the alkalis to be compared must be of the same concentration. For example:
10 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide: pH = 13
10 mol dm-3 ammonia solution: pH = 11 - For two different alkalis of the same concentration, the alkali with the higher pH value is the stronger alkali, i.e. higher degree of ionisation in water.