What is the Relationship between Electric Current and Potential Difference?
- When an electric charge is placed at a point in an electric field, it experiences an electric force acting on it. Work is required to move the electric charge in the electric field against this force. This charge is said to have an electric potential at that point.
- Figure shows two points, A and B on an electric field line of a positively-charged sphere. Point A, which is nearer to the sphere, has a higher potential than point B.
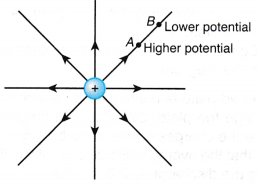
- When a positive test charge is placed at point A, the positive charge will move away from point A (higher potential) to point B (lower potential).
- If you want to move the positive charge from point B to point A, work or energy is required to move the charge against the electric field. This work done to move one unit of charge from point B to point A is known as the potential difference between the two points.
- Similarly, when a battery is connected to a bulb in a circuit, as shown in Figure, it creates a potential difference, that is, a difference in the potential energy of the charges in the conductors connected to its terminals. When the switch is off, the positive terminal, P is at a higher potential and the negative terminal Q is at a lower potential. When the switch is on, the potential difference between the two terminals causes the charges to flow across the bulb in the circuit and light up the bulb.
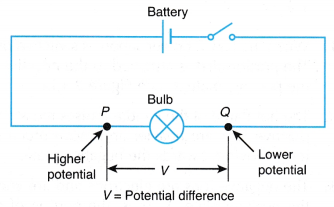
- The energy carried by the charges will be converted into other forms of energy such as light and heat energy in the bulb. So work is done when electrical energy carried by the charges is dissipated as heat and light energy after crossing the bulb.
- The potential difference between two points in an electric field is defined as the work done or the energy that would be required to move one coulomb of charge from one point to another.
- In symbols:
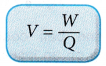 Where, V = potential difference (p.d.) in volt (V)
Where, V = potential difference (p.d.) in volt (V)
W = work done in driving the charge between the two points in joule (J)
Q = amount of positive charges in coulomb (C) - The SI unit for potential difference is volt (V).
- The potential difference between two points in an electric field is one volt, if the work done to move one coulomb of charge between the two points is one joule.
People also ask
- What is Electric Current?
- What is an electric field and how is it created?
- Electromotive Force, Internal Resistance & Potential Difference of a Cell/Battery
- How series and parallel circuits are different?
- Relationship between Energy Transferred, Current, Voltage and Time
- Power Rating and Energy Consumption of Various Electrical Appliances
Relationship between Electric Current and Potential Difference Problems with Solutions
- When a charged metal dome of a Van de Graaff generator is discharged through a resistive wire, it is found that 2 C of charge passes through it and it dissipates 12 000 J of energy. What is the potential difference across the wire?
Solution:
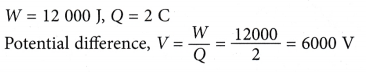
- In a closed circuit, a 6 V battery is used to drive 40 C of electric charges through a light bulb.
(a) How much work is done to drive the charges through the bulb?
(b) What is the current that flows in the circuit in 20 minutes?
Solution:
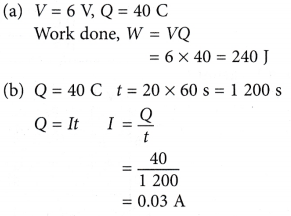
Relationship between Potential Difference and Current Experiment
Aim: To investigate the relationship between current and potential difference for a metal wire.
Problem: When a current passes through a conductor such as a metal wire, bulb and diode, electrical energy is converted into heat energy causing a potential difference across the conductor. What is the relationship between potential difference across a conductor and the current that passes through it?
Hypothesis: When the current that passes through a metal wire increases, the potential difference across the metal wire increases.
Variables:
(a) Manipulated variable: Current, I
(b) Responding variable: Potential difference, V
(c) Fixed variable: Length and type of metal wire
Materials: 50 cm constantan wire (s.w.g. 24)
Apparatus: Ammeter (0 – 1 A), voltmeter (0 – 5 V), battery holder, three 1.5 V batteries, rheostat, switch, connecting wires
Method:
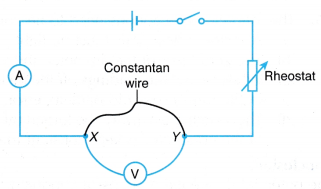
- The battery, ammeter, voltmeter and rheostat are connected in a circuit as shown in Figure. The 50 cm constantan wire is connected across terminals X and Y.
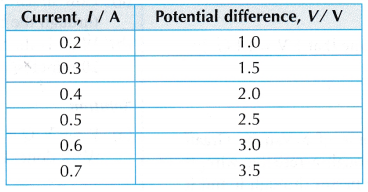
- The circuit is switched on and the rheostat is adjusted until the ammeter gives a reading, I = 0.2 A. The potential difference, V across XY is recorded from the voltmeter.
- Step 2 is repeated by adjusting the rheostat to fix the current at I = 0.3 A, 0.4 A, 0.5 A, 0.6 A and 0.7 A. The corresponding values of potential difference across the wire are recorded.
- All the values are recorded in a table.
- A graph of V versus I is plotted. Both- axes must begin from the origin.
Results:
- Tabulation of results.
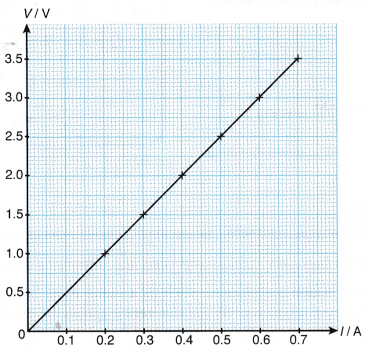
- Graph of V against I.
Discussion:
- As more charges carrying electrical energy passes through the conductor per unit time, more electrical energy is dissipated. Hence, the potential difference, V across the conductor increases with the current, I that flows through it.
- The graph of V against I is a straight-line graph that passes through the origin showing that the potential difference, V is directly proportional to the current, I (V ∝ I).
- The gradient or the ratio of V/I is constant as current increases.
- A small current (less than 1 A) is used throughout the experiment so that the conductor is not heated up and its temperature can be assumed constant.
- The following precautions need to be considered during the experiment:
(a) All wire connections must be tightly fixed and the length of the wire should not be too long.
(b) The zero error of the ammeter and voltmeter must be checked and adjusted.
(c) While taking the readings off the meters, make sure that the pointer is always vertically above its image in the mirror to avoid parallax error.
(d) The switch must always be turned off when not taking any reading. This is to ensure that the temperature of the conductor is kept constant throughout the experiment.
Conclusion:
The potential difference, V across a conductor increases when the current, I passing through it increases as long as the conductor is kept at a constant-temperature. The hypothesis is accepted.