Order in Homologous Series
- Photograph shows the first members of various homologous series.
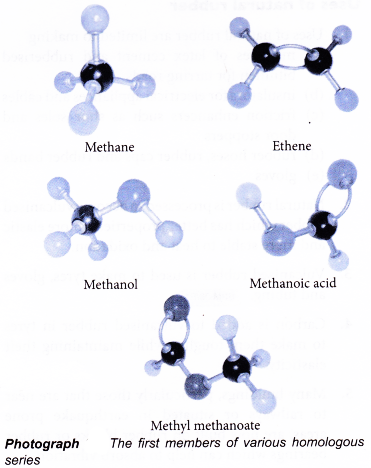
- Alkanes, alkenes, alcohols, carboxylic acids and esters belong to different homologous series. The organisation of organic compounds into the various different homologous series makes the study of organic chemistry more systematic, orderly and effective.
- The members of any homologous series have properties that vary in a regular and predictable manner. There is order in all homologous series with respect to the nomenclature, physical properties and chemical properties.
Systematic naming of organic compounds
All members of a homologous series are named systematically following the IUPAC rules. The IUPAC name of an organic molecule provides information about
- which homologous series it belongs to
- its functional group
- the total number of carbon atoms present
- its molecular and structural formulae
Order in physical and chemical properties
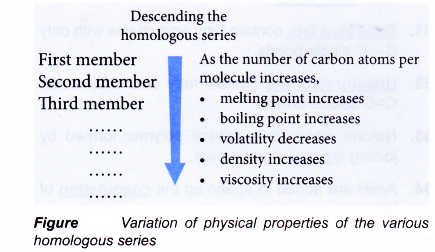
- The physical properties of members of a homologous series show very regular pattern. These properties change gradually as the number of carbon atoms increases. Figure summarises the trend or order in the variation of physical properties of the various homologous series.
- Each homologous series has its own functional group. These functional groups determine the chemical reactions that an organic molecule can undergo. Hence, all members of a homologous series have very similar chemical properties.
For example,- the carbon-carbon double bond allows all members of the alkene homologous series to undergo addition reactions.
- acidic properties of carboxylic acids are due to the presence of the carboxyl group,
- The order in the physical and chemical properties of organic molecules in a homologous series makes it easy to predict the properties and behaviour of unknown members of the series. By studying the properties of a few members of a homologous series, it is possible to deduce the properties of the other members in the same series.
People also ask
- What are carbon compounds?
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- How are alkanes formed?
- What is an alkene in chemistry?
- What is an isomerism?
- What is alcohol and how is it made?
- How are carboxylic acids formed?
- How esters are formed?
- What are fats and oils?
- How palm oil is extracted?
- What is the monomer of natural rubber?
- Which acid is used for coagulating rubber from latex?
- Classification of Hydrocarbons
- What is the homologous series of hydrocarbons?
- Properties and Uses of Ethanol
- Properties and Uses of Ethanoic Acid