Math Labs with Activity – Pythagoras theorem (Method 1)
OBJECTIVE
To verify Pythagoras’ theorem (Method 1)
Materials Required
- A piece of cardboard
- Two sheets of white paper
- A pair of scissors
- A geometry box
- A tube of glue
Theory
Pythagoras’ theorem: In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Procedure
Step 1: Paste a sheet of white paper on the cardboard. On this paper, draw a right-angled triangle ABC, right angled at C. Let the lengths of the sides AB, BC and CA be c, a and b units respectively.
Step 2: On the other sheet of paper draw three squares—one with each side measuring a units, another with each side measuring b units and the third with each side measuring c units. Cut these three squares and place them along the sides of the right-angled ΔABC as shown in Figure 9.1.
Step 3: Label the diagram as shown in Figure 9.1.
Step 4: Draw the diagonals CD and AE of the square of side b units. Let these diagonals intersect at a point O.
Step 5: Through O, draw MN||AB. Also, draw PQ⊥MN such that PQ passes through O (see Figure 9.1).
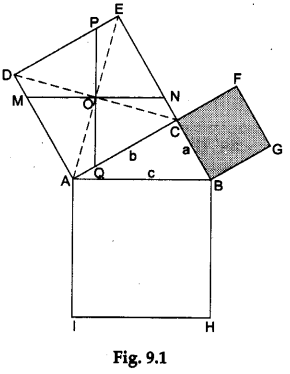
Step 6: Remove the squares DECA and CFGB from their existing positions. Cut the square DECA along the lines MN and PQ to get four quadrilaterals. Now, arrange these four quadrilaterals along with the square CFGB on the square ABHI as shown in Figure 9.2.
What do you observe?
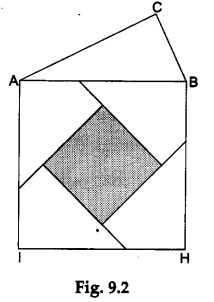
Observations and Calculations
The four quadrilaterals along with the square CFGB completely cover the square ABHI.
∴ area of the square ABHI = area of the square CFGB + sum of areas of the four quadrilaterals
=> area of the square ABHI = area of the square CFGB + area of the square DECA
=> c² =a² + b².
So, the square of the hypotenuse of the right-angled ΔABC is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Result
Pythagoras’ theorem is verified.
Math Labs with ActivityMath LabsScience Practical SkillsScience Labs