What is the Relationship Between Temperature and Pressure?
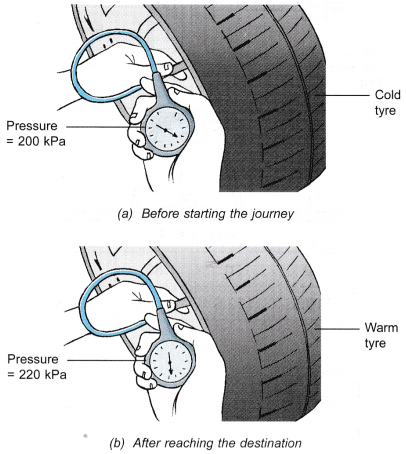
- Figure (a) shows a man measuring the pressure of the air in his car tyre before starting on a long journey. After reaching his destination, he measured the pressure again and the pressure gauge showed that the pressure had increased, as shown in Figure (b). He touched the tyre and found that it was warm.
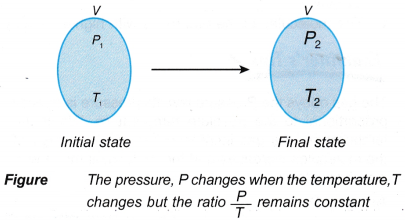
- The Pressure Law (Gay-Lussac’s Law) gives the relationship between the pressure and temperature of a fixed mass of gas at constant volume.
- The relationship between pressure and temperature can be explained using the kinetic theory of gases.
(a) When a gas is heated, the average kinetic energy of the molecules increases. The temperature of the gas increases.
(b) The faster moving molecules strike the walls of the container more frequently.
(c) The molecules experience a larger change of momentum when they bounce back from the walls.
(d) A larger force is exerted on the walls.
(e) Since the surface area of the walls remains constant, a higher pressure now acts on the walls. - The Pressure Law states that for a fixed mass of gas, the pressure of the gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature when its volume is kept constant.
- The mathematical expression for the pressure law:
 that is, the ratio, P/T = constant, when the volume is kept constant.
that is, the ratio, P/T = constant, when the volume is kept constant.
- The equation for Pressure law is:

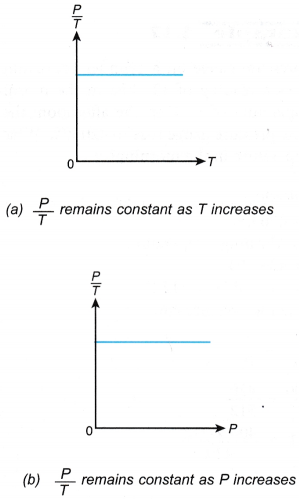
- The relationship between the pressure and the absolute temperature of a gas under constant volume can also be expressed by the graphs in Figure.
People also ask
What is the Charles Law?
What is the Boyle’s law?
Experiment:
Aim: To determine the relationship between the pressure and the temperature of a fixed mass of gas at constant volume.
Problem: What is the relationship between the pressure and the temperature of a fixed mass of gas at constant volume?
Inference: The temperature of a gas affects its pressure.
Hypothesis: The pressure of a fixed mass of gas increases when the temperature is increased.
Variables:
(a) Manipulated variable: Temperature
(b) Responding variable: Pressure of the air
(c) Fixed variables: The mass of the air in the flask and the volume
Operational Definition: The thermometer measures the temperature of the water. Since the water and the air in the flask are in thermal equilibrium, the reading of the thermometer is defined operationally as the temperature of the air in the flask.
Material: Water
Apparatus: Bourdon gauge, round bottom flask, large beaker, thermometer, tripod stand with wire gauze, Bunsen burner, stirrer
Method:
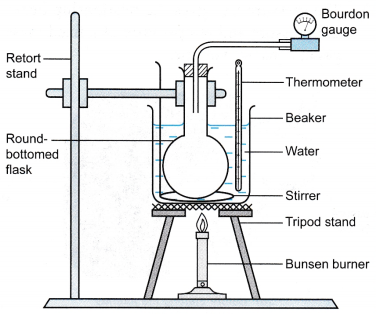
- The apparatus is set up as shown in Figure.
- The water in the beaker is heated slowly and stirred continuously.
- When the temperature is θ = 30°C, the pressure of the air, P is read from the Bourdon gauge.
- Steps 2 and 3 are repeated for values of temperature, θ = 40°C, 50°C, 60°C, 70°C, 80°C and 90°C.
- The readings are tabulated. A graph of pressure, P against temperature, θ is plotted.
Results:
- Tabulation of results.
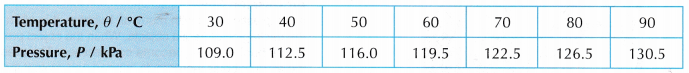
- Graph of P against θ.
Discussion:
- The water was stirred continuously so that its temperature was uniform.
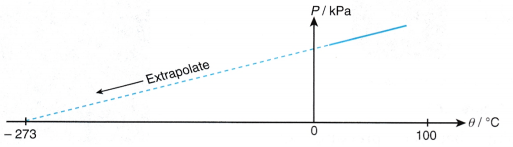
- The graph of pressure, P against temperature, 9 is a straight line which does not pass through the origin. At 0°C, the molecules of the air are still moving and a pressure is exerted on the walls of the container.
- When the straight line is extrapolated, it is found that the pressure becomes zero at -273°C.
- The temperature -273°C is the lowest possible temperature. There is no other condition with a lower degree of coldness than -273°C.
- Therefore, the temperature of -273°C is known as the absolute zero of temperature.
- The Kelvin scale of temperature begins at absolute zero with the value 0 kelvin (0 K).
- Temperatures measured on the kelvin scale are known as absolute temperatures.
- The relationship between temperature in kelvin and degrees Celsius for three common temperatures are as listed in Table.
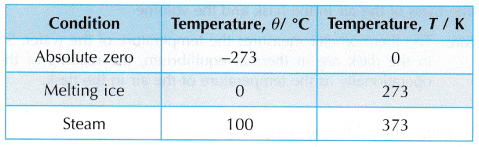
- Temperatures in °C can be converted to K by adding 273:
θ°C = (θ + 273) K - A change in temperature of 1°C.is equal to a change in temperature of 1 K.
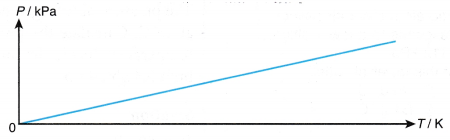
- When the temperature of a gas is expressed in kelvins, the graph of pressure against absolute temperature is a straight line passing through the origin, as shown in Figure.
Conclusion:
The pressure of the gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. The hypothesis is accepted.
Gay-Lussac’s Law Example Problems with Solutions
Example 1. A pressure gauge on a cylinder containing oxygen shows a reading of 400 kPa in the morning. At a temperature of 39°C in the afternoon, the reading of the pressure gauge rose to 420 kPa. What was the temperature in the morning?
Solution:

Example 2. The pressure of nitrogen gas in a light bulb is 60 kPa at 25°C. Calculate the pressure of the gas when the temperature inside the bulb rises to 167°C after the bulb is lighted up.
Solution:
