What Is The Cartesian Coordinate System
In Cartesian co-ordinates the position of a point P is determined by knowing the distances from two perpendicular lines passing through the fixed point. Let O be the fixed point called the origin and XOX’ and YOY’, the two perpendicular lines through O, called Cartesian or Rectangular co-ordinates axes.
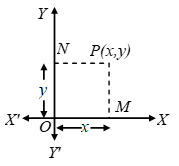 Draw PM and PN perpendiculars on OX and OY respectively. OM (or NP) and ON (or MP) are called the x-coordinate (or abscissa) and y-coordinate (or ordinate) of the point P respectively.
Draw PM and PN perpendiculars on OX and OY respectively. OM (or NP) and ON (or MP) are called the x-coordinate (or abscissa) and y-coordinate (or ordinate) of the point P respectively.
- Axes of Co-ordinates
In the figure OX and OY are called as x-axis and y-axis respectively and both together are known as axes of co-ordinates. - Origin
It is point O of intersection of the axes of co-ordinates. - Co-ordinates of the Origin
It has zero distance from both the axes so that its abscissa and ordinate are both zero. Therefore, the coordinates of origin are (0, 0). - Abscissa
The distance of the point P from y-axis is called its abscissa. In the figure OM = PN is the Abscissa. - Ordinate
The distance of the point P from x-axis is called its ordinate. ON = PM is the ordinate in the figure. - Quadrant
The axes divide the plane into four parts. These four parts are called quadrants. So, the plane consists of axes and quadrants. The plane is called the cartesian plane or the coordinate plane or the xy-plane. These axes are called the co-ordinate axes.
A quadrant is 1/4 part of a plane divided by co-ordinate axes.
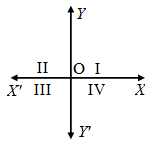
(i) XOY is called the first quadrant
(ii) YOX’ the second.
(iii) X’OY’ the third.
(iv) Y’OX the fourth
as marked in the figure.
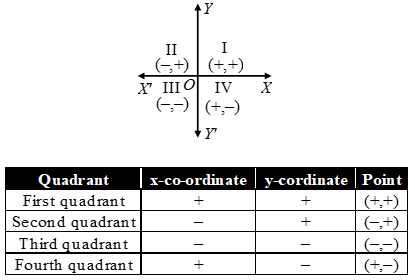
RULES OF SIGNS OF CO-ORDINATES
- In the first quadrant, both co-ordiantes i.e., abscissa and ordinate of a point are positive.
- In the second quadrant, for a point, abscissa is negative and ordinate is positive.
- In the third quadrant, for a point, both abscissa and ordinate are negative.
- In the fourth quadrant, for a point, the abscissa is positive and the ordinate is negative.
Cartesian Coordinate System Example Problems With Solutions
Example 1: From the adjoining figure find
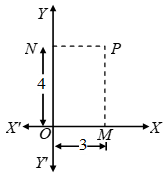
(i) Abscissa
(ii) Ordinate
(iii) Co-ordinates of a point P
Solution: (i) Abscissa = PN = OM = 3 units
(ii) Ordinate = PM = ON = 4 units
(iii) Co-ordinates of the point P = (Abscissa, ordinate) = (3, 4)
Example 2: Determine
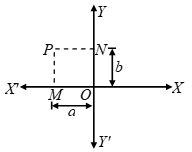
(i) Abscissa (ii) ordinate (iii) Co-ordinates of point P given in the following figure.
Solution: (i) Abscissa of the point P = – NP = –OM = – a
(ii) Ordinate of the point P = MP = ON = b
(iii) Co-ordinates of point P = (abscissa, ordinate)
= (–a, b)
Example 3: Write down the (i) abscissa (ii) ordinate (iii) Co-ordinates of P, Q, R and S as given in the figure.
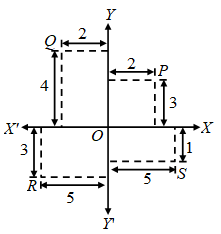
Solution: Point P
Abscissa of P = 2; Ordinate of P = 3
Co-ordinates of P = (2, 3)
Point Q
Abscissa of Q = – 2; Ordinate of Q = 4
Co-ordinate of Q = (–2, 4)
Point R
Abscissa of R = – 5; Ordinate of R = – 3
Co-ordinates of R = (–5, –3)
Point S
Abscissa of S = 5; Ordinate of S = – 1
Co-ordinates of S = (5, – 1)
Example 4: Draw a triangle ABC where vertices A, B and C are (0, 2), (2, – 2), and (–2, 2) respectively.
Solution: Plot the point A by taking its abscissa O and ordinate = 2.
Similarly, plot points B and C taking abscissa 2 and –2 and ordinates – 2 and 2 respectively. Join A, B and C. This is the required triangle.
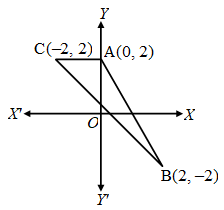
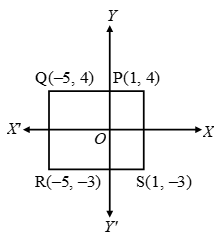
Example 5: Draw a rectangle PQRS in which vertices P, Q, R and S are (1, 4), (–5, 4), (–5, –3) and
(1, – 3) respectively.
Solution: Plot the point P by taking its abscissa 1 and ordinate – 4.
Similarly, plot the points Q, R and S taking abscissa as –5, –5 and 1 and ordinates as 4, – 3 and –3 respectively.
Join the points PQR and S. PQRS is the required rectangle.
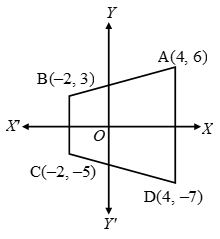
Example 6: Draw a trapezium ABCD in which vertices A, B, C and D are (4, 6), (–2, 3), (–2, –5) and
(4, –7) respectively.
Solution: Plot the point A taking its abscissa as 4 and ordinate as 6.
Similarly plot the point B, C and D taking abscissa as – 2, –2 and 4 and ordinates as 3, – 5, and –7 respectively. Join A, B, C and D ABCD is the required trapezium.