What is a Wave?
- Figure shows water waves being formed when a few drops of water fall onto the surface of a pond.

- Figure shows water waves being formed when a few drops of water fall onto the surface of a pond.
- A wave is a travelling disturbance from a vibrating or oscillating source. As a wave travels, it carries energy along with it in the direction of its propagation.
- The two basic types of waves are transverse waves and longitudinal waves.
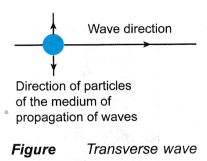
- A transverse wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium move in the direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave moves. Figure shows a transverse wave. Examples of transverse waves are water waves and electromagnetic waves.
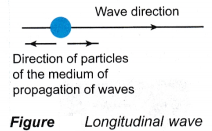
- A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium move in the direction parallel to the direction in which the wave moves. Figure shows a longitudinal wave. An example of longitudinal waves is sound waves.
What is the Wavefront?
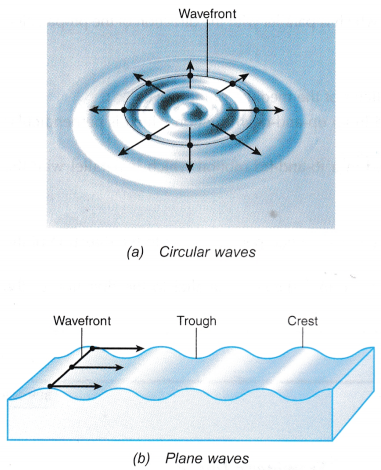
- Figure shows the circular and plane wavefronts of water waves respectively.
- A wavefront is an imaginary line that joins all identical points on a wave.
- The direction of the propagation of a wave is perpendicular to its wavefront.
How does a wave transfer energy without transferring matter?
Aim: To study the characteristics of waves.
Materials: Polystyrene beads, water
Apparatus: Ripple tank and its accessories
Method:
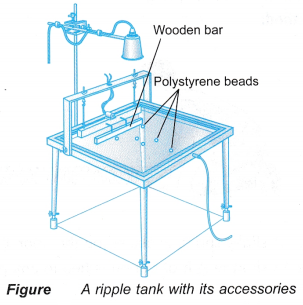
- A ripple tank with its accessories is set up and filled with water.
- Some polystyrene beads are placed on the water surface.
- The rheostat is adjusted so that the wooden bar moves up and down slowly to create straight waves travelling away from the wooden bar.
- The movement of the polystyrene beads is observed.
Observation:
The polystyrene beads move up and down as the waves move forward. Figure illustrates the motion of the waves and the polystyrene beads.
 Discussion:
Discussion:
As the waves move forward, the polystyrene beads do not move forward. Instead, they vibrate about their respective positions.
Conclusion:
Waves transfer energy without transferring matter.
From the above experiment, we can see that although the wave energy moves from the vibrating source, the particles are not carried along with the wave. Hence, waves transfer energy without transferring matter.