Understanding Elasticity
Figure shows some objects around us that are elastic.

Elasticity is a property of matter that enables an object to return to its original size and shape when the forces that are acting on it are removed. Figure shows the elastic property of an object.
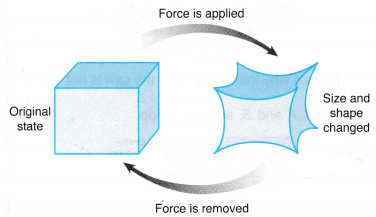 The elasticity of a solid is due to, the strong inter-molecular forces between the molecules of the solid as explained in Figure.
The elasticity of a solid is due to, the strong inter-molecular forces between the molecules of the solid as explained in Figure.

Experiment 1
Aim: To investigate the relationship between force and the extension of a spring.
Problem: Figure shows three babies of different weights lying in a cradle attached to a spring of the same type. What is the relationship between the force and the extension of a spring?

Hypothesis: The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the applied force.
Variables:
(a) Manipulated variable: Force
(b) Responding variable: Extension of the spring
(c) Fixed variable: Type of spring (The same spring is used throughout the experiment)
Operational Definition: The extension of a spring is defined as:
Extension, x = The length of the extended spring – The original length of the spring
Materials: Steel spring, slotted masses, holder of slotted masses, pin, plasticine.
Apparatus: Metre rule, retort stand with two clamps, G-clamp.
Method:
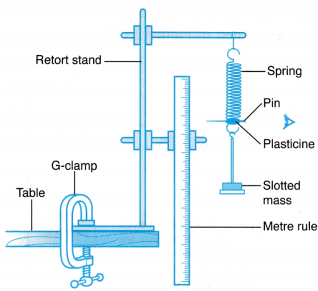
- The apparatus is set up as shown in Figure.
- The initial position of the pin is marked when no mass is attached to the spring.
- A slotted mass, m = 40 g is attached to the end of the spring and the new position of the spring is
- compared to its initial position. The extension of the spring, x is measured.
- Step 3 is repeated using slotted masses of mass, m = 60 g, 80 g, 100 g and 120 g.
- A graph of extension, x against force, F is plotted.
Results:
1. Tabulation of results.
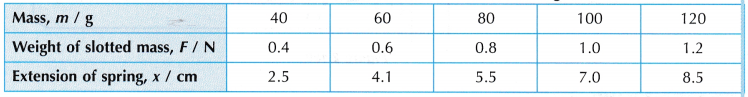
2. Based on the results in Table, the graph of x against F is plotted.

Discussion:
1. The graph of x against F in Figure is a straight line with a positive gradient and passes through the origin.
2. This shows that the extension of a spring is directly proportional to the applied force. The hypothesis is accepted.
Conclusion:
The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the applied force.
Factors that Affect Elasticity
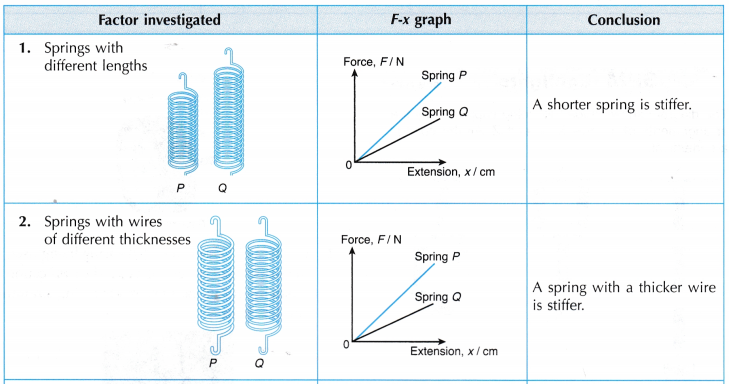
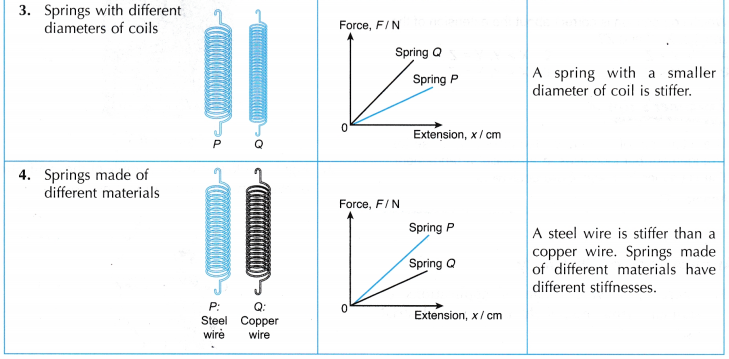
- Springs come in different sizes and stiffness according to their uses. A spring used in a ballpoint pen is smaller than and not as stiff as the one used in a motorcycle suspension system as shown in Figure.

- The elasticity of springs can be studied by comparing the stiffness of each spring. A stiffer spring requires a bigger force to cause the same amount of extension. Hence, it has a bigger stiffness constant, k.
- Figure shows a comparison of two springs, P and Q.
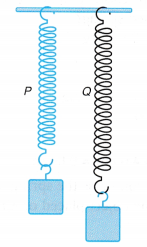
(a) Both the springs have the same natural length. They are attached to loads of equal weight.
(b) Spring Q is extended more than spring P. This means that with the same amount of force, spring Q is stretched more than spring P.
(c) We can also say that to stretch both the springs, P and Q, to the same amount of extension, a larger force is needed for spring P.
(d) We can conclude that spring P is stiffer and has a larger stiffness constant, k than spring Q. - Figure shows the F-x graphs of the two springs, P and Q, plotted on the same axes.

- By comparing the gradients of the two graphs, spring P has a larger stiffness constant, k than spring Q. Hence, spring P is stiffer than spring Q.
Aim: To study the factors that affect the elasticity of a spring.
Materials: A pair of steel springs with different lengths, a pair of steel springs with wires of different thickness, a pair of steel springs with different diameters of coils, a steel spring and a copper spring of the same size, five sets of springs of the same size, 10 sets of 100 g slotted masses with holders, 10 pins, plasticine.
Apparatus: Two metre rules, two retort stands-with clamps, two C-clamps
Method:
The apparatus is set up as shown in Figure for each spring in the pair.
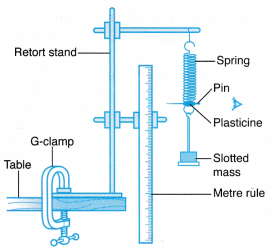
The initial position of the pins are marked when no masses are attached to the pair of steel springs with different lengths.
An F-x graph is plotted for each spring for comparison.
Steps 2 and 3 are repeated for springs with wires of different thicknes, springs with different diameters of coils, springs of different materials and springs with different arrangements.
When a factor is being investigated, the other factors are kept constant.
Discussion:

Applications of Elasticity
- There is a wide range of applications of elasticity, from household usage to industrial use.
- Figure shows a coiled spring being used in the suspension system of a car. The application of elasticity in this case has made riding smoother and less bumpy.
- Figure shows an example of the application of elasticity for a recreational purpose.

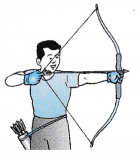
- Figure shows an athlete aiming at a target with his bow and arrow. The elastic bow is an example of the application of elasticity in sports.
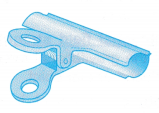
- The double clip, in Figure, which is normally used in the office, is an example of the application of elasticity in the office.
- Figure shows other applications of elasticity:
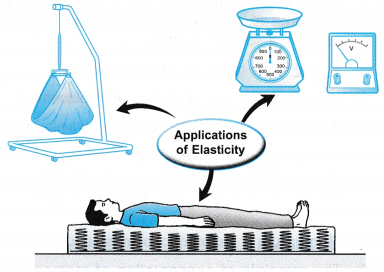
- (a) Baby cradles use springs to rock babies to sleep.
(b) Weighing machines and meters use springs to return the pointer to its original position.
(c) Spring mattresses make sleeping more comfortable by supporting the weight of a person sleeping on it. The springs enable the mattress to return to its original size and shape when the person rises from the bed.