ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 8 Ratio and Proportion Chapter Test
These Solutions are part of ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths. Here we have given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 8 Ratio and Proportion Chapter Test.
ML Aggarwal SolutionsICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
Find the compound ratio of:
(a + b)2 : (a – b )2 ,
(a2 – b2) : (a2 + b2),
(a4 – b4) : (a + b)4
Solution:
(a + b)2 : (a – b )2 ,
(a2 – b2) : (a2 + b2),
(a4 – b4) : (a + b)4

Question 2.
If (7 p + 3 q) : (3 p – 2 q) = 43 : 2 find p : q
Solution:
(7p + 3q) : (3p – 2q) = 43 : 2
=> \(\frac { 7p+3q }{ 3p-2q } =\frac { 43 }{ 2 } \)

Question 3.
If a : b = 3 : 5, find (3a + 5b): (7a – 2b).
Solution:
a : b = 3 : 5
=> \(\frac { a }{ b } =\frac { 3 }{ 5 } \)
3a + 5n : 7a – 2b
Dividing each term by b
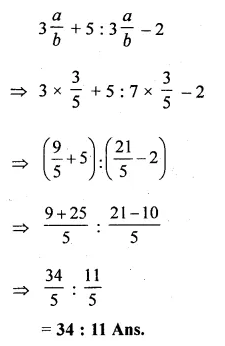
Question 4.
The ratio of the shorter sides of a right angled triangle is 5 : 12. If the perimeter of the triangle is 360 cm, find the length of the longest side.
Solution:
Let the two shorter sides of a right angled triangle be 5x and 12x.
Third (longest side)

Question 5.
The ratio of the pocket money saved by Lokesh and his sister is 5 : 6. If the sister saves Rs 30 more, how much more the brother should save in order to keep the ratio of their savings unchanged ?
Solution:
Let the savings of Lokesh and his sister are 5x and 6x.
and the Lokesh should save Rs y more Now, according to the problem,
=> \(\frac { 5x+y }{ 6x+30 } =\frac { 5 }{ 6 } \)
=> 30x + 6y = 30x + 150
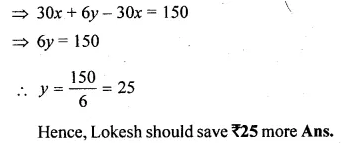
Question 6.
In an examination, the number of those who passed and the number of those who failed were in the ratio of 3 : 1. Had 8 more appeared, and 6 less passed, the ratio of passed to failures would have been 2 : 1. Find the number of candidates who appeared.
Solution:
Let number of passed = 3 x
and failed = x
Total candidates appeared = 3x + x = 4x. In second case
No. of candidates appeared = 4 x + 8
and No. of passed = 3 x – 6
and failed = 4x + 8 – 3x + 6 = x + 14
then ratio will be = 2 : 1
Now according to the condition
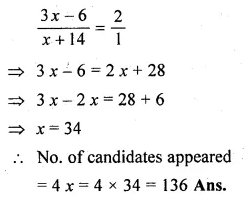
Question 7.
What number must be added to each of the numbers 15, 17, 34 and 38 to make them proportional ?
Solution:
Let x be added to each number, then numbers will be 15 + x, 17 + x, 34 + x, and 38 + x.
Now according to the condition

Question 8.
If (a + 2 b + c), (a – c) and (a – 2 b + c) are in continued proportion, prove that b is the mean proportional between a and c.
Solution:
(a + 2 b + c), (a – c) and (a – 2 b + c) are in continued proportion
=> \(\frac { a+2b+c }{ a-c } =\frac { a-c }{ a-2b+c } \)

Question 9.
If 2, 6, p, 54 and q are in continued proportion, find the values of p and q.
Solution:
2, 6, p, 54 and q are in continued proportional then
=> \(\frac { 2 }{ 6 } =\frac { 6 }{ p } =\frac { p }{ 54 } =\frac { 54 }{ q } \)

Question 10.
If a, b, c, d, e are in continued proportion, prove that: a : e = a4 : b4.
Solution:
a, b, c, d, e are in continued proportion
=> \(\frac { a }{ b } =\frac { b }{ c } =\frac { c }{ d } =\frac { d }{ e } \) = k (say)

Question 11.
Find two numbers whose mean proportional is 16 and the third proportional is 128.
Solution:
Let x and y be two numbers
Their mean proportion = 16
and third proportion = 128

Question 12.
If q is the mean proportional between p and r, prove that:
\({ p }^{ 2 }-{ 3q }^{ 2 }+{ r }^{ 2 }={ q }^{ 4 }\left( \frac { 1 }{ { p }^{ 2 } } -\frac { 3 }{ { q }^{ 2 } } +\frac { 1 }{ { r }^{ 2 } } \right) \)
Solution:
q is mean proportional between p and r
q² = pr
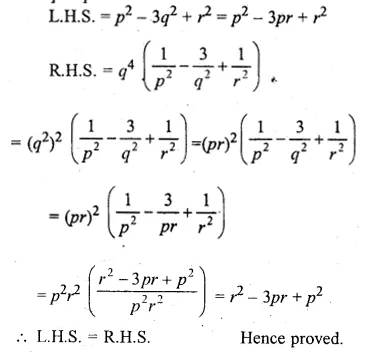
Question 13.
If \(\frac { a }{ b } = \frac { c }{ d } = \frac { e }{ f } \), prove that each ratio is
(i) \(\sqrt { \frac { { 3a }^{ 2 }-{ 5c }^{ 2 }+{ 7e }^{ 2 } }{ { 3b }^{ 2 }-{ 5d }^{ 2 }+{ 7f }^{ 2 } } } \)
(ii) \({ \left[ \frac { { 2a }^{ 3 }+{ 5c }^{ 3 }+{ 7e }^{ 3 } }{ { 2b }^{ 3 }+{ 5d }^{ 3 }+{ 7f }^{ 3 } } \right] }^{ \frac { 1 }{ 3 } } \)
Solution:
\(\frac { a }{ b } = \frac { c }{ d } = \frac { e }{ f } \) = k(say)
∴ a = k, c = dk, e = fk

Question 14.
If \(\frac { x }{ a } = \frac { y }{ b } = \frac { z }{ c } \), prove that
\(\frac { { 3x }^{ 3 }-{ 5y }^{ 3 }+{ 4z }^{ 3 } }{ { 3a }^{ 3 }-{ 5b }^{ 3 }+{ 4c }^{ 3 } } ={ \left( \frac { 3x-5y+4z }{ 3a-5b+4c } \right) }^{ 3 }\)
Solution:
\(\frac { x }{ a } = \frac { y }{ b } = \frac { z }{ c } \) = k (say)
x = ak,y = bk,z = ck
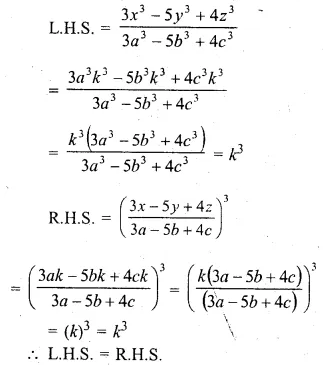
Question 15.
If x : a = y : b, prove that
\(\frac { { x }^{ 4 }+{ a }^{ 4 } }{ { x }^{ 3 }+{ a }^{ 3 } } +\frac { { y }^{ 4 }+{ b }^{ 4 } }{ { y }^{ 3 }+{ b }^{ 3 } } =\frac { { \left( x+y \right) }^{ 4 }+{ \left( a+b \right) }^{ 4 } }{ { \left( x+y \right) }^{ 3 }+{ \left( a+b \right) }^{ 3 } } \)
Solution:
\(\frac { x }{ a } = \frac { y }{ b } \) = k (say)
x = ak, y = bk
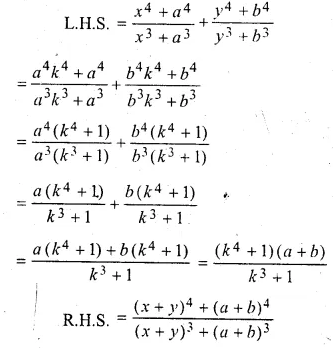
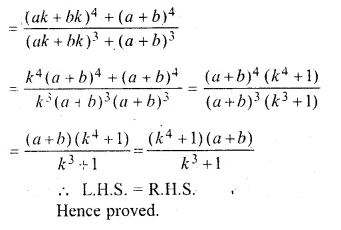
Question 16.
If \(\frac { x }{ b+c-a } =\frac { y }{ c+a-b } =\frac { z }{ a+b-c } \) prove that each ratio’s equal to :
\(\frac { x+y+z }{ a+b+c } \)
Solution:
\(\frac { x }{ b+c-a } =\frac { y }{ c+a-b } =\frac { z }{ a+b-c } \) = k(say)
x = k(b + c – a),
y = k(c + a – b),
z = k(a + b – c)
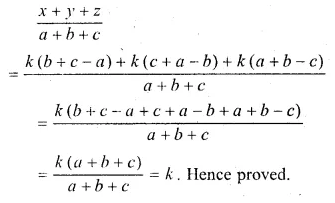
Question 17.
If a : b = 9 : 10, find the value of
(i) \(\frac { 5a+3b }{ 5a-3b } \)
(ii) \(\frac { { 2a }^{ 2 }-{ 3b }^{ 2 } }{ { 2a }^{ 2 }+{ 3b }^{ 2 } } \)
Solution:
a : b = 9 : 10
=> \(\frac { a }{ b } = \frac { 9 }{ 10 }\)

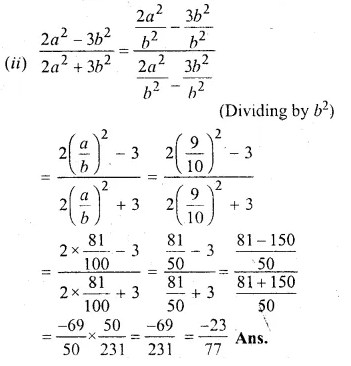
Question 18.
If (3x² + 2y²) : (3x² – 2y²) = 11 : 9, find the value of \(\frac { { 3x }^{ 4 }+{ 25y }^{ 4 } }{ { 3x }^{ 4 }-{ 25y }^{ 4 } } \) ;
Solution:
\(\frac { { 3x }^{ 4 }+{ 25y }^{ 4 } }{ { 3x }^{ 4 }-{ 25y }^{ 4 } } =\frac { 11 }{ 9 } \)
Applying componendo and dividendo

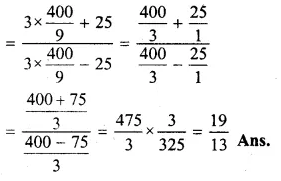
Question 19.
If \(x=\frac { 2mab }{ a+b } \) , find the value of
\(\frac { x+ma }{ x-ma } +\frac { x+mb }{ x-mb } \)
Solution:
\(x=\frac { 2mab }{ a+b } \)
=> \(\frac { x }{ ma } +\frac { 2b }{ a+b } \)
Applying componendo and dividendo

Question 20.
If \(x=\frac { pab }{ a+b } \) ,prove that \(\frac { x+pa }{ x-pa } -\frac { x+pb }{ x-pb } =\frac { 2\left( { a }^{ 2 }-{ b }^{ 2 } \right) }{ ab } \)
Solution:
\(x=\frac { pab }{ a+b } \)
=> \(\frac { x }{ pa } +\frac { b }{ a+b } \)
Applying componendo and dividendo
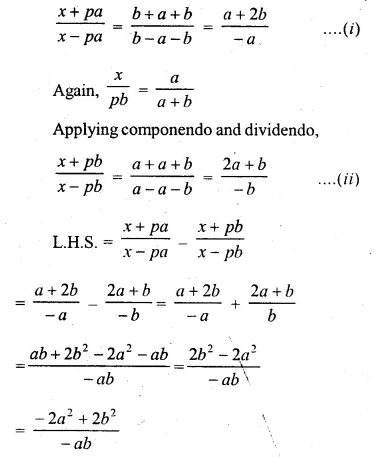

Question 21.
Find x from the equation \(\frac { a+x+\sqrt { { a }^{ 2 }-{ x }^{ 2 } } }{ a+x-\sqrt { { a }^{ 2 }-{ x }^{ 2 } } } =\frac { b }{ x } \)
Solution:
\(\frac { a+x+\sqrt { { a }^{ 2 }-{ x }^{ 2 } } }{ a+x-\sqrt { { a }^{ 2 }-{ x }^{ 2 } } } =\frac { b }{ x } \)
Applying componendo and dividendo,


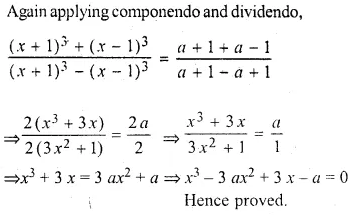
Question 22.
If \(x=\frac { \sqrt [ 3 ]{ a+1 } +\sqrt [ 3 ]{ a-1 } }{ \sqrt [ 3 ]{ a+1 } -\sqrt [ 3 ]{ a-1 } } \), prove that :
x³ – 3ax² + 3x – a = 0
Solution:
\(x=\frac { \sqrt [ 3 ]{ a+1 } +\sqrt [ 3 ]{ a-1 } }{ \sqrt [ 3 ]{ a+1 } -\sqrt [ 3 ]{ a-1 } } \)
Applying componendo and dividendo,

Question 23.
If \(\frac { by+cz }{ b^{ 2 }+{ c }^{ 2 } } =\frac { cz+ax }{ { c }^{ 2 }+{ a }^{ 2 } } =\frac { ax+by }{ { a }^{ 2 }+{ b }^{ 2 } } \), prove that each of these ratio is equal to \(\frac { x }{ a } =\frac { y }{ b } =\frac { z }{ c } \)
Solution:
\(\frac { by+cz }{ b^{ 2 }+{ c }^{ 2 } } =\frac { cz+ax }{ { c }^{ 2 }+{ a }^{ 2 } } =\frac { ax+by }{ { a }^{ 2 }+{ b }^{ 2 } } \)


Hope given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 8 Ratio and Proportion Chapter Test are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. APlusTopper try to provide online math tutoring for you.