What is heat of displacement?
- When a more electropositive metal displaces a less electropositive metal from a solution of its salt, heat change occurs.
- The heat of displacement is the heat change when one mole of a metal is displaced from its salt solution by a more electropositive metal.
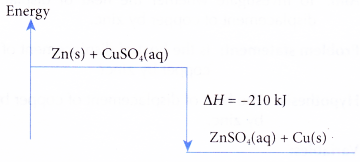
- The thermochemical reaction for the displacement reaction of copper by zinc can be represented as follows.
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) ΔH = -210 kJ
(a) When one mole of copper is displaced from its salt solution by zinc, 210 kJ of heat is given out.
(b) The heat of displacement of copper by zinc is -210 kJ mol-1.
(c) The energy level diagram for the displacement reaction of copper by zinc is shown in Figure.
(d) As the copper is displaced by zinc, the intensity of the blue solution decreases until it becomes colourless. - The heat of displacement of a metal can be determined by measuring the heat change occurred when a more electropositive metal in excess is added to a known quantity of a salt solution of a less electropositive metal.
- The heat of displacement of a metal is different when it is displaced by different metals in the electrochemical series.
- For example, the heat of displacement of silver by magnesium is higher than the heat of displacement of silver by zinc. This is because magnesium is more electropositive than zinc.
People also ask
- How can energy be changed in a chemical reaction?
- How does the energy level diagram show this reaction is exothermic?
- What is enthalpy of reaction?
- What is heat of precipitation?
- What is the enthalpy of neutralization?
- What is the heat of combustion?
- Why is energy released when a bond is formed?
- Applications of exothermic and endothermic reactions in everyday life
- What is meant by the calorific value of a fuel?
Heat of Displacement Experiment
Aim: To investigate whether the heat of displacement of copper by magnesium is higher than the heat of displacement of copper by zinc.
Problem statement: Is the heat of displacement of copper by magnesium higher than the heat of displacement of copper by zinc?
Hypothesis: The heat of displacement of copper by magnesium is higher than the heat of displacement of copper by zinc.
Variables:
(a) Manipulated variable : Different metals used to displace copper
(b) Responding variable : Heat of displacement of copper
(c) Controlled variables : Volume and concentration of copper(II) sulphate solution, plastic cup, mass of metals
Materials: 0.2 mol dm-3 copper(II) sulphate solution, magnesium powder, zinc powder.
Apparatus: Thermometer, plastic cup with cover, 50 cm3 measuring cylinder, electronic balance, weighing bottle.
Procedure:
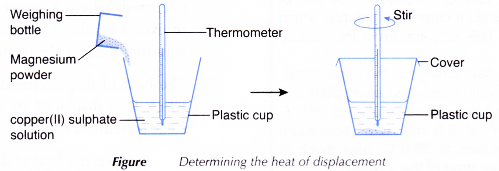
- 50 cm3 of 0.2 mol dm-3 copper(II) sulphate solution is measured and poured into a plastic cup.
- The initial temperature of the solution is measured and recorded after a few minutes.
- About 2 g of magnesium powder is weighed in a weighing bottle.
- The magnesium powder is then added quickly and carefully into the copper(II) sulphate solution.
- The mixture in the plastic cup is stirred using the thermometer and the highest temperature reached is recorded.
- Steps 1 to 5 are repeated using zinc powder to replace the magnesium powder with other factors remain unchanged.
Results:

Interpreting data:
1. Heat of displacement of copper by magnesium
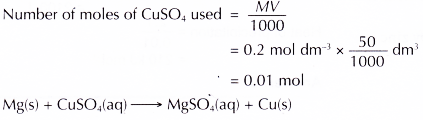
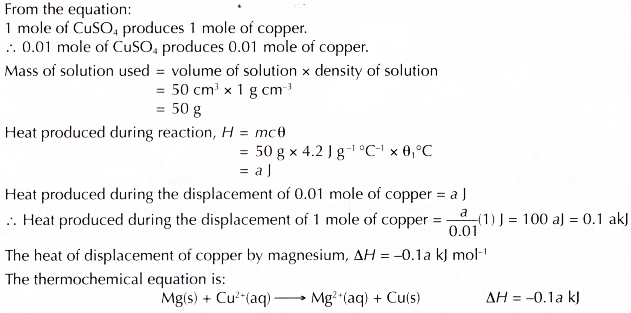
2. Heat of displacement of copper by zinc
Discussion:
- Magnesium and zinc are more electropositive than copper, therefore both magnesium and zinc can displace copper from copper(II) sulphate solution.
- In both the reactions, brown solids (copper metal) are formed. The intensity of the blue solutions decreases until they become colourless.
- The equations for the reactions are shown below.
(a) Displacement of copper by magnesium:
Chemical equation : Mg(s) + CuSO4(aq) → MgSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Ionic equation : Mg(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + Cu(s)
(b) Displacement of copper by zinc:
Chemical equation : Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
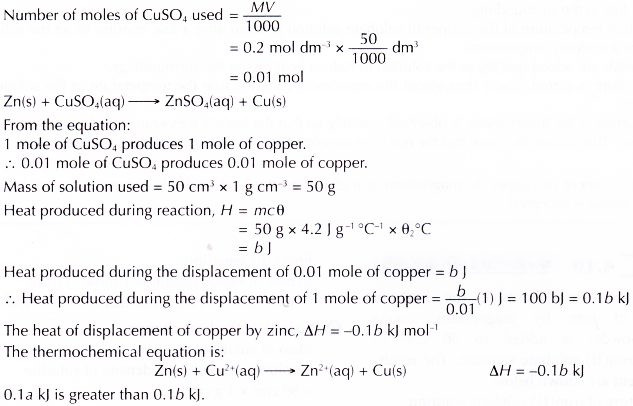
Ionic equation : Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) - The theoretical values of heat of displacement of copper for both the reactions are shown below.
Mg(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + Cu(s) ΔH = -352 kJ
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) ΔH= -210 kJ - The energy level diagrams for both reactions are shown below.
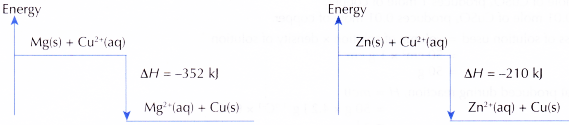
- Excess magnesium and zinc are used to make sure all the copper(II) ions are displaced to form copper.
- The amount of heat absorbed by the remaining unreacted magnesium and zinc is very little and can be neglected in the calculation of the heat of displacement.
- The volume and concentration of copper(II) sulphate solution used in both reactions are the same so that the same number of moles of copper is formed.
- The following precautions need to be taken during the experiment to get more accurate results.
(a) Metals in the powder form are used so that the reactions will take a shorter time to complete, and thus less heat is lost to the surroundings.
(b) The initial temperature of the copper(II) sulphate solution is taken after a few minutes to let the solution achieve a uniform temperature.
(c) The metals are added quickly to the solution to reduce heat loss to the surroundings.
(d) The mixture is stirred slowly throughout the experiment to make sure the temperature of the solution is uniform.
(e) The reading of the thermometer is observed carefully so that the highest temperature of the solution can be recorded. This is done to ensure that the reactions are completed and all the heat has been given out.
Conclusion:
The heat of displacement of copper by magnesium is higher than the heat of displacement of copper by zinc.
Hence, the hypothesis is accepted.
Heat of Displacement Calculation – Problems with Solutions
1. In an experiment to determine the heat of displacement of iron by magnesium, excess magnesium powder is added to 50 cm3 of 0.2 mol dm-3 iron(II) sulphate solution. The results of the experiment are shown below.
Initial temperature of iron(II) sulphate solution = 30.5°C
Highest temperature of the mixture = 40.0°C
Calculate the heat of displacement of iron.
[Specific heat capacity of solution: 4.2 J g-1 °C-1; density of solution: 1 g cm-3]
Solution:

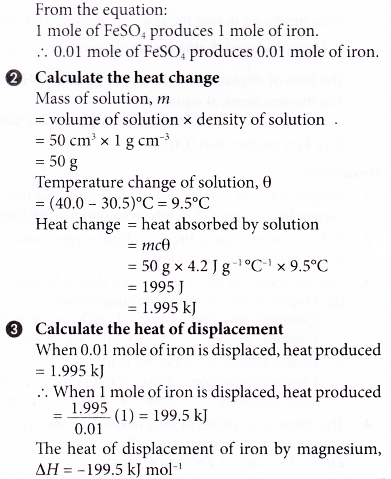
2. 1.4 g of iron powder is added to 200 cm3 of 1.5 mol dm-3 copper(II) sulphate solution at an initial temperature of 29.0°C. The thermochemical equation is as follows.
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s) ΔH = -150 kJ
What is the highest temperature of the mixture?
[Specific heat capacity of solution: 4.2] g-1 °C-1. Density of solution: 1 g cm-3. Relative atomic mass: Fe, 56]
Solution:

