How is glass produced from raw materials?
Glass
- The raw material for making glass is sand (silicon dioxide or silica) which is abundant in the Earth’s crust.
- Glass is formed when silicon dioxide is melted and mixed with other substances like lead(II) oxide, boron oxide, sodium carbonate or calcium carbonate.
- Generally, glass can be made by heating a mixture of silicon dioxide and metal carbonates to a temperature above 1500°C.
(a) When sodium carbonate and calcium carbonate are heated to a high temperature, they decompose to form oxides.
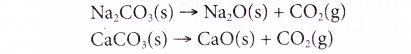
(b) The metal oxides then combine with silicon dioxide to form the respective metal silicates.
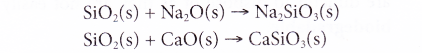
(c) The overall reaction is as follows:
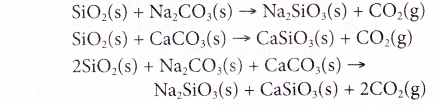
(d) Thus, glass is actually a metal silicate or a mixture of metal silicates such as sodium silicate and calcium silicate. - In glass, every silicon atom is bonded covalently by four oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral manner. Every oxygen atom is also bonded to two silicon atoms to form a three-dimensional gigantic covalent molecule.
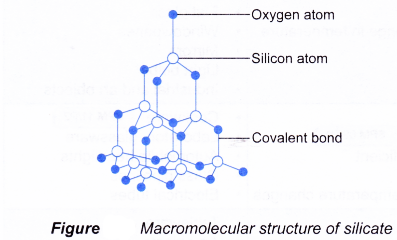
- The physical properties of glass depend on the percentage of the various silicates present. Generally, all types of glass have the following common properties:
(a) Transparent
(b) Hard but brittle
(c) Impermeable to liquid
(d) Heat insulator
(e) Bad conductor of electricity
(f) Chemically inert - There are different types of glass depending on what is added to silicon dioxide. There are fused glass, soda-lime glass, borosilicate glass and lead crystal glass.
- Fused glass
(a) Fused glass is made from pure silicon dioxide by heating it to a temperature above 1700°C until it becomes molten and then cooled quickly.
(b) During fast cooling, the SiO4 tetrahedral do not have time to crystallise out to form regular structure. Thus, the structure resembles that of a liquid state. Hence, glass is a super-cooled liquid.
(c) Fused glass is expensive because exceptionally high temperature is required during its manufacture.
(d) Fused glass consists mainly of silica. Thus, it is the simplest glass. - Soda-lime glass
(a) Soda-lime glass is made by heating a mixture of sand, SiO2 (silica) with limestone, CaCO3, sodium carbonate, Na2CO3 and recycled glass (sodium silicate, Na2SiO3 and calcium silicate, CaSiO3) at around 1500°C and cooling it quickly.
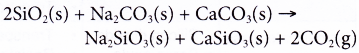
(b) The presence of sodium silicate makes the glass melts at a much lower temperature.
(c) It is the most common and earliest used glass. - Borosilicate glass
(a) Borosilicate glass is obtained when boron oxide (B2O3) is added to soda-lime glass.
(b) Borosilicate glass has a higher melting point and a lower coefficient of expansion and can withstand a wider range of temperature change due to the presence of borosilicate.
(c) The less alkali content makes it more resistant to chemical attack than soda-lime glass. This explains why borosilicate glass is excellent for chemical and electrical uses. - Lead crystal glass
(a) Lead crystal glass is made by substituting lead oxide with calcium oxide and often with part of the silica used in soda-lime glass.
(b) The presence of lead(II) silicate makes the glass denser, has higher refractive index and is much more expensive than soda-lime glass.
(c) Lead crystal glass is normally called crystal or lead glass.
People also ask
- How ceramics are made?
- How is a composite material made?
- How polymers are classified?
- What is alloy metal?
Composition, Properties and Uses of Glass
Table summarises the composition, properties and uses of the four types of glass.
| Type of glass | Composition | Properties | Uses |
| Fused glass |
|
|
|
| Soda-lime glass |
|
|
|
| Borosilicate glass |
|
|
|
| Lead crystal glass |
|
|
|