What is stoichiometry and why is it used in chemistry?
- Stoichiometry is a study of quantitative composition of substances involved in the chemical reactions.
- A balanced chemical equation can be used to calculate number of moles, number of particles and mass or volume of a reactant or product.
- By using the information obtained from a balanced chemical equation, it is possible to calculate the quantities of reactants used or the quantities of products formed in the reaction.
- Generally, the steps involved in the stoichiometric calculations are as follows.
(1) Write down the balanced equation of the reaction.
(2) Gather information from the question. If necessary, convert the given unit to the number of moles.
(3) Based on the equation, compare the ratio of moles of the related substances.
(4) Calculate the answer proportionately. Then, convert the answer to the required unit.
People also ask
- How do you Write a Chemical Equation?
- What is the Relative Atomic Mass and Relative Molecular Mass of an Element?
- What is One Mole and How many Particles are in a Mole?
- How do you Calculate the Molar Mass of a Substance?
- What is the Molar Volume of a Gas at STP?
- How do you know the Order of Elements in a Chemical Formula
- What is Empirical and Molecular Formula?
Stoichiometry Problems with Answers
1. How many moles of potassium are needed to react with 0.5 mole of bromine gas?
2K(s) + Br2(g) ⟶ 2KBr(s)
Solution:

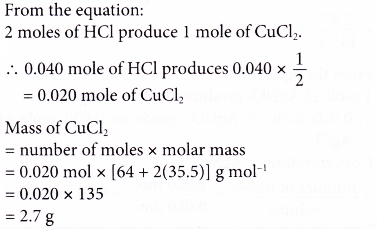
2. Ethene gas burns in excessive oxygen according to the following equation.
C2H4(g) + 3O2(g) ⟶ 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
Find the volume of carbon dioxide released at STP if 42 g of ethene is burnt completely. [Relative atomic mass: H, 1; C, 12. Molar volume: 22.4 dm3 mol-1 at STP]
Solution:
3. What is the mass of zinc needed to produce 2.4 dm3 of hydrogen gas at room conditions?
Zn(s) + 2HNO3(aq) ⟶ Zn(NO3)2(aq) + H2(g)
[Relative atomic mass: Zn, 65. Molar volume: 24 dm3 mol-1 at room conditions]
Solution:

4. Aluminium reacts with copper(II) oxide to produce aluminium oxide and copper. If 2.0 g of excess aluminium is reacted with 0.06 mole of copper(II) oxide, find the mass of aluminium left after the reaction.
[Relative atomic mass: Al, 27]
Solution:

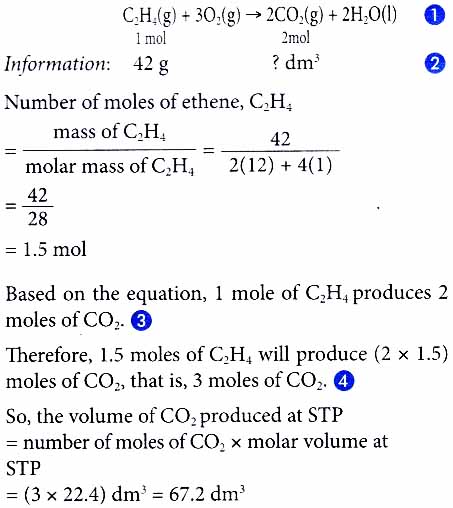
5. Excess sodium chloride is added to 50.0 cm3 of silver nitrate solution. 2.87 g of silver chloride is precipitated. Calculate the concentration of the silver nitrate solution in mol dm-3.
[Relative atomic mass: Cl, 35.5; Ag, 108]
Solution:
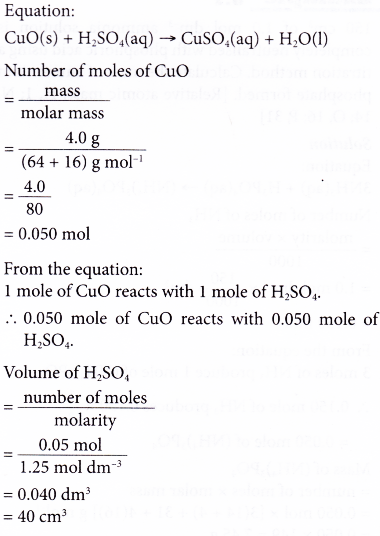
6. In the preparation of copper(II) sulphate, a student added 4.0 g of copper(II) oxide to 1.25 mol dm-3 sulphuric acid. Calculate the volume of the acid needed to react completely with the copper(II) oxide. [Relative atomic mass: O, 16; Cu, 64]
Solution:
7. Excess aluminium powder is added to 300 cm3 of 2.0 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid. The mixture is then warmed to speed up the reaction. Calculate the mass of the salt formed. [Relative atomic mass: Al, 27; Cl, 35.5]
Solution:

8. 150 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 ammonia solution is completely neutralised with phosphoric acid using a titration method. Calculate the mass of ammonium phosphate formed. [Relative atomic mass: H, 1; N, 14; O, 16; P, 31]
Solution:

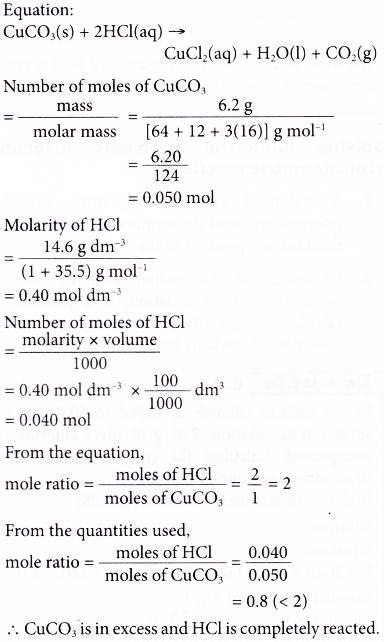
9. 6.20 g of copper(II) carbonate is added to 100 cm3 of 14.6 g dm-3 hydrochloric acid. Calculate the mass of copper(II) chloride produced. [Relative atomic mass: H, 1; C, 12; O, 16; Cl, 35.5; Cu, 64]
Solution: