Selina Concise Biology Class 9 ICSE Solutions Pollination and Fertilization
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 5 Pollination And Fertilization. You can download the Selina Concise Biology ICSE Solutions for Class 9 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Biology for Class 9 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Download Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 5 Pollination And Fertilization
Exercise 1
Solution A.
- (c) Stigma and anthers mature at the same time
- (b) Pollen grain
Solution B.1.
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Generative nucleus | (i) Male nuclei |
| (b) Germ pore | (ii) Pollen tube |
| (c) Exine | (iii) Rough |
| (d) Secondary nucleus | (iv) Endosperm nucleus |
| (e) Integument | (v) Testa |
| (f) Egg nucleus | (vi) Fertilization |
Solution B.2.
(a) butterflies
(b) wind
(c) water
Solution B.3.
(a) autogamy
(b) dichogamy
(c) Vallisneria
Solution B.4.
(a) Ovules
(b) Ovary
(c) Ovarian wall
Solution B.5.
(a) Bisexual flower
(b) Inflorescence
(c) Self-pollination/Autogamy
(d) Dichogamy
(e) Heterostyly
(f) Entomophily
(g) Ornithophily
Solution C.1.
(a) Ornithophily-Pollination affected by birds
(b) Elephophily-Pollination affected by elephants
(c) Artificial pollination-Pollination affected by man through artificial means
Solution C.2.
(a) Ovules-Seed
(b) Calyx-Falls off or remains intact in dried and shrivelled form
(c) Petals-Fall off
(d) Stamens-Fall off
Solution C.3.
Contrivances in flowers which favour cross-pollination:
- Unisexuality
- Different timings of maturation ofandroeciumand gynoecium
- Self-sterility
- Structural barriers
Solution D.1.
(a) Long and feathery stigma: Help to trap pollen grains in wind-pollination
(b) Brightly coloured petals: Attracting insects for cross-pollination
(c) Smooth and light pollen: Easily carried by wind to enable cross-pollination
(d) Protruding and easily movable anthers: Even slightest wind can move them
(e) Fragrant nectar: Attracting insects for pollination
Solution D.2.
Advantages of cross-pollination:
- The offspring are healthier.
- The seeds produced are abundant and viable.
- New varieties may be produced by cross-pollinating two different varieties of the same species.
Disadvantages of cross-pollination:
- Pollination is not always certain.
- The pollen has to be produced in large quantity.
- The process is uneconomical for the plant because the flowers have to be large,coloured, scented and have to produce nectar for attracting pollinating agents.
Solution E.1.
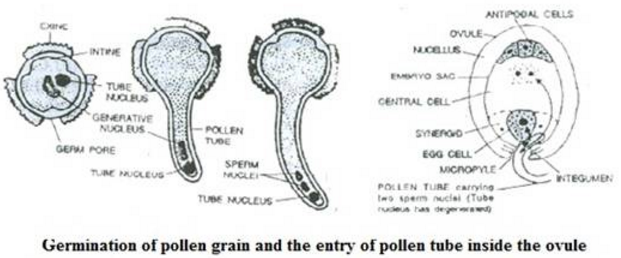
The pollen tube grows out of the pollen grains by breaking through its exine. The pollen tube grows through the stigma and style by dissolving these tissues with the help of enzymes and reaches the ovary, where it enters the ovule through a minute pore called the micropyle.
Solution E.2.
a)
1 → Exine
2 → Intine
3 → Pollen tube
4 → Tube nucleus
5 → Generative nucleus
(b) Germination of the pollen grain takes place only after it falls on the stigma of the same plant species. The pollen grain is stimulated to germinate due to the secretion of sugars by the stigma.
(c) The function of part ‘4’ (tube nucleus) is to direct the growth of the pollen tube towards the ovary.
(d) During germination of the pollen grain, part ‘5’ (generative nucleus) present at the tip of the pollen tube divides into two sperm nuclei. The pollen tube enters one of the synergids and releases its two sperm nuclei. Of these, one sperm nucleus enters the egg cell and fuses with its nucleus, while the other sperm nucleus moves towards the two polar nuclei in the central cell and fuses with them.
Solution E.3.
(a)
1 → Style
2 → Pollen tube
3 → Polar nuclei
4 → Embryo sac
5 → Antipodal cells
6 → Micropyle
(b) After fertilisation
(i) The ovary enlarges to form the fruit and the ovarian wall forms the fruit wall.
(ii) The ovule becomes the seed.
(c) Synergids help in nourishing the egg cell, guiding the pollen tube towards the egg, proper functioning of the pollen tube and release of sperm nuclei.
(d) Pollen grain is transferred to the stigma during pollination. Germination of pollen grain takes place only if it falls on the stigma. After germination, the pollen tube grows through the stigma and reaches the ovary for the fertilisation of the egg cell.
More Resources for Selina Concise Class 9 ICSE Solutions
- Concise Biology Class 9 ICSE Solutions
- Concise Chemistry Class 9 ICSE Solutions
- Concise Physics Class 9 ICSE Solutions
- Concise Mathematics Class 9 ICSE Solutions