Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 14 Biomolecules is part of Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Year Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 14 Biomolecules.
Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 14 Biomolecules
Question 1.
Carbohydrates can be divided into three major classes monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. (March – 2010)
a) What are polysaccharides?
b) Give two examples for polysaccharides.
c) What is invert sugar?
Answer:
a) Polysaccharides are carbohydrates which on hydrolysis gives large number of monosaccharide units.
b) Starch and cellulose
c) The equimolar mixture of D – (+) – glucose and D – (-) fructose obtained by the hydrolysis of sucrose is called invert sugar.
Question 1.
Glucose (C6H12O6) is a monosaccharide, which can be oxidized, reduced and acetylated. What happens when glucose is treated with the following: (Say – 2010)
a) Br2 water
b) Hl/red P
c) Acetic anhydride
Answer:
a) When glucose is treated with bromine water it is oxidised to gluconic acid.
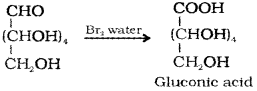
b) Glucose on prolonged heating with HI forms n-Hexane.
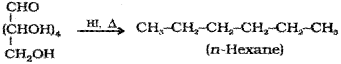
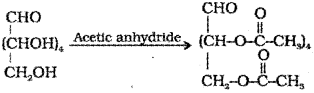
c) Acetylation of glucose with acetic anhydride gives glucose pentaacetate.
Question 1.
a) Names of some carbohydrates, their properties and structural patterns are given below. Match them properly. (March – 2011)
| Glucose | Disaccharide | d-1, 4 link |
| Sucrose | Reducing | Galactoxide |
| Lactose | Insoluble (in water) | 1, 6-linkage |
| Amylopectin | Non-reducing | Fructoxide |
| Trisaccharide | Anomers present | |
| Mono saccharide | 2-glucose units linked |
b) Proteins have polypeptide bonds. What are polypeptides?
Answer:
a) Glucose – monosaccharide – Anomers present Sucrose – Disaccharide – Fructoxide Lactose – Reducing -1,4 link Amylopectin – Insoluble in water -1,6 link
b) When the number of amino acid units in a protein is more than ten, then the products are called polypeptides.
Question 1.
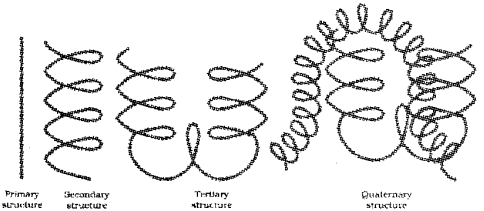
Proteins are the polymers of a-amino acids. The structure and shape of proteins can be discussed at four different levels, namely, primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Give an account of structure and shape of proteins considering the above four levels. (Say – 2011)
Answer:
The structure and shape of proteins can be studied at four different levels, i.e., primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary.
1) Primary structure of proteins – It refers to the se-quence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
2) They are found to exist in two different types of structures such as α -helix and β-pleated sheet structure. In α -helix the polypeptide chain forms all possible hydrogen bonds by twisting into a right-handed screw with the -NH groups of each amino acid residue hydrogen-bonded to the ![]() gnoup of an adjacent tum of the helix. In β -pleated sheet structure all peptide chains are stretched out to nearly maximum extension and laid side by side which are held together by intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
gnoup of an adjacent tum of the helix. In β -pleated sheet structure all peptide chains are stretched out to nearly maximum extension and laid side by side which are held together by intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
3) Tertiary structure of proteins – It represents overall folding of the polypeptide chains.
4) Quaternary structure of proteins – The spacial arrangement of two or more polypeptide chains.
Question 1.
a) Carbohydrates are classified into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. (March – 2012)
i) What is the basis of such classification? Explain.
ii) Give an example for an oligosaccharide.
b) Vitamin ‘C’ is a vitamin found in fruits and v egetables. It cannot be stored in our body. Why?
Answer:
a) i) On the basis of their behaviour on hydrolysis, carbohydrates are divided in to three major classes.
1) Monosaccharides : These cannot be hy-drolysed further into simpler unit of polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone. e.g. Glucose, Fructose etc.
2) Oligosaccharides : These carbonydrates which on hydrolysis give 2-10 monosaccharide units. e.g. Sucrose
3) Polysaccharides: These are high molecular mass carbohydrates which give many monosaccharide units on hydrolysis. e.g. Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen etc. ii) Sucrose
b) Vitamin ‘C’ is a water soluble vitamin and must be supplied regularly in diet because they are readily excreted in urine and cannot be stored in our body.
Question 1.
Proteins are important polymers of biological systems. (Say – 2012)
i) What is the denaturation of proteins?
ii) Give two examples of denaturation.
Answer:
i) When a protein in its native is subjected to physical change like change in temperature or chemical change like change in pH, the hydrogen bonds are distrubed, the 2° and 3° structures change and the protein loses its biological activity. This is called denaturation of the protein.
ii) 1) When egg is boiled, it becomes hard because the soluble globular proteins change to in-soluble fibrous proteins.
2) Curdling of milk which is caused due to the formation of lactic acid by the bacteria present in milk.
Question 1.
a) Amino acids can be classified into essential amino acids and non-essential amino acids. (March – 2013)
i) What is the basis of such classification?
ii) Write one example each for essential and non-essential amino acids.
b) Write any two differences between DNA and RNA.
Answer:
a) i) The amino acids which can be synthesized in body are known as non-essential amino acids. Those amino acids which can not be synthesized in body and must be obtained through diet are known as essential amonoacids.
ii) Essential amino acids
e.g. Valine, Lysine
Non -essential amino acids
e.g. Glycine, Alanine
b)
| DNA | RNA |
| 1) Double helix structure 2) Sugar- deoxyribose 3) Bases – A, G, C, T 4) Transmits Traits | 1) Single helix 2) Sugar-Ribose 3) Bases A,G, C ,U 4) Responsible for protein synthesis |
Question 1.
Name the products obtained in the following reactions. (Say – 2013)
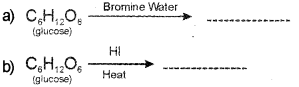
c) What is inverted sugar?
d) Name two polysaccharides.
Answer:
a) Gluconic acid.
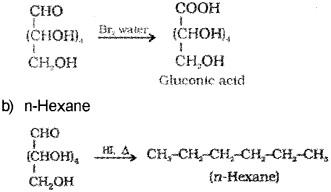
c) The equimolar mixture of D – (+) – glucose and D – (-) fructose obtained by the hydrolysis of sucrose is called invert sugar.
d) starch and cellulose
Question 1.
Biomolecules are formed by certain specific linkages between simple monomeric units. Write the names of linkages and monomeric units in the following class of biomolecules. (March – 2014)
i) Starch
ii) Protein
iii) Nucleic acid
Answer:
i) Starch – Monomer: α – D – (+) – Glucose
Linkage: Glycosidic linkage
ii) Protein – Monomer: α – amino acids
Linkage : Peptide linkage or Peptide bond
iii) Nucleic acid – Monomer: Nucleotide
Linkage: Phosphodiesterlinkage
Question 1.
a) Name a fast soluble vitamin. Suggest a disease caused by its deficiency. (Say – 2014)
b) What do you mean by the following :
i) Secondary structure of proteins.
ii) Nucleosides.
Answer:
a) Vitamin A-Xerophthalmia
b) i) It refers to the shape in which a long polypeptide chain can exist. These are found to exist in two different types of structures viz. α-helix and β -pleated sheet structure. These structures arise due to the regular folding of the backbone of the polypeptide chain due to hydrogen bonding between and NH- groups of the peptide bond.
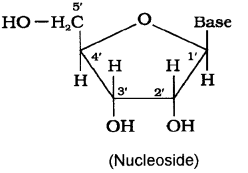
ii) Nucleoside is a structural part of nucleic acid. It is a unit formed by the attachment of a base to 1′ position of sugar.
Question 1.
Carbohydrates are broadly divided into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. (March – 2015)
a) Write one example each of monosaccharide and oligosaccharide.
b) i) Write any one method for the preparation of glucose.
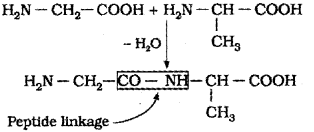
ii) What is peptide linkage?
Answer:
a) Monosaccharide – Glucose, Fructose, Ribose (anyone) Oligosaccharide – Sucrose, Maltose, Lactose (any one)
b) i) From Sucrose (cane sugar): Sucrose on hydrolysis gives glucose and fructose.
or
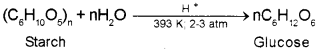
Hydrolysis of starch by boiling it with dilute H2SO4 at 393 K under pressure.
ii) Due to peptide linkage an amide farmed between -COOH group and -NH2 group of amino acids of proteins.
Question 1.
a) Match the following structures of proteins in Column 1 with their characteristic features in column II. (Say – 2015)
b) What is the denaturation of proteins?
Answer:
a)
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Primary structure | (a) Special arrangement of polypeptide subunits |
| (ii) Secondary structure | (b) Structure of amino acids |
| (iii) Tertiary structure | (c) Folding of peptide chains |
| Civ) Quaternary structure | (d) Sequence of amino acids |
| (e) Fibrous or globular nature |
b) What is the denaturation of proteins?
Answer:
a)
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Primary structure (ii) Secondary structure (iii) Tertiary structure (iv) Quaternary structure | (d) Sequence of amino acids (c) Folding of peptide chains (e) Fibrous and globular nature (a) Spacial arrangement of polypeptide subunits |
b) When a protein in its native form, is subjected to physical change like change in temperature or chemical change like change in pH, the hydrogen bonds are disturbed. Due to this, globules unfold and helix get uncoiled and protein loses its biological activity. This is called denaturation of pretein.
Question 1.
Cane Sugar, Glucose and Starch are Carbohydrates. (March – 2016)
a) Represent the structure of Glucose.
b) Write a method to prepare Glucose from Starch. Write the chemical equation of the reaction.
c) Suggest any two uses of Carbohydrates.
Answer:
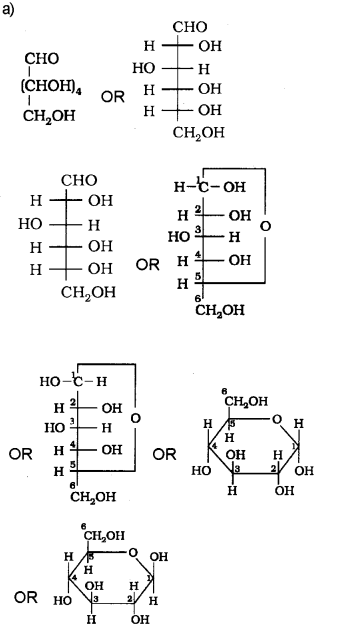
b) Glucose is obtained by hydrolysis of starch by boiling it with dilute H2SO4 at 393 K under pressure.
c)
- Carbohydrates form a major portion of our food.
- Honey, a carbohydrate has been used for a long time as an instant source of energy ¡n ayurvedic system of medicine.
- Carbohydrates are used as storage molecules as starch in plants and glycogen in animals.
- Cell wall of bacteria and plants is made up of cellulose.
- Cellulose in the form of cotton fibre is used for clothing.
- Cellulose in the form of wood is used to build furniture.
- Carbohydrates provide raw materials for many important industries like textiles, paper, lacqures and breweries. (any two)
Question 1.
Proteins are biomolecules (Say – 2016)
a) What is denaturation of protein?
b) Match the following:
Vitamin A – Glucose
Starch – Zymase
Aldohexose – Night blindness
Enzyme – Amylose
– Fructose
Answer:
a) When a protein in its native form is subjected to physical change like change in temperature or chemical change like change in pH, the hydrogen bonds are disturbed. Due to this, globules unfold and helix get uncoiled and protein loses its biological activity. This is called denaturation of protein.
b) VitaminA – Night blindness
Starch – Amylose
Aldohexose – Glucose
Enzyme – Zymase
Question 1.
a) Which of the following is a polysaccharide? (March – 2017)
i) Maltose
ii) Sucrose
iii) Fructose
iv) Cellulose
b) Explain the amphoteric behaviour of amino acid.
Answer:
a) iv) Cellulose
b) This behaviour is due to the presence of both acidic (carboxyl group) and basic (amino group) groups in the same molecule. In aqueous solution, the carboxyl group can lose a proton and amino group can accept a proton, giving rise to a dipolar ion known as a zwitterion. In zwitterionic form, amino c:ds show amphoteric behaviour as they react both with acids and bases.
Question 1.
a) a -D-(+) glucose and p -D(+) glucose are (Say – 2017)
i) Metameres
ii) Anomers
iii) Geometrical Isomers
iv) Functional group isomers
b) What is the denaturation of proteins?
c) Differentiate between nucleoside and nucleotide
Answer:
a) ii) Anomers
b) When a protein is treated with acid, alkali or heated or subjected to change in pH, the secondary and primary structure of protein gets ruptured. Denaturation does not change the primary structure of proteins.
c) The repeating structural units of nucleic acids are called nucleotides.
Pentose sugar + Base → nucleoside
Nucleoside + Phosphoric acid → nucleotide
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 14 Biomolecules help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 14 Biomolecules, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.