Kerala Plus Two Microeconomics Chapter Wise previous Questions Chapter 5 Market Equilibrium
Question 1.
Compared to rural areas, the wage rate is higher in urban areas. Discuss the reasons for this. (MARCH-2008)
Answer:
Wages are higher in urban areas compared to rural areas due to the following reasons.
- Availability of skilled workers in urban areas.
- Professionals in urban areas.
- Occupational and geographical mobility.
- Differences in risks in certain urban jobs.
Question 2.
When you conducted a survey among teachers working in parallel colleges in Trichur district it is found that there exist difference in earnings among teachers teaching different subjects. Find the reason for the same with suitable examples. (MAY-2009)
Answer:
Wage differences are due to the following reasons.
- Difference in skill and productivity
- People are not the same in matter of tastes, talents and efficiency.
- Occupational and geographical mobility.
- Some professions require high cost and long period of training.
- Difference in risks involved in certain jobs.
- Due to these reasons, some are paid more and others are paid less.
Question 3.
Suppose demand and supply curve of good x shift simultaneously. The simultaneous shift can happen in four possible cases. The impact on equilibrium price and quantity in all the four cases are different. On the basis of this, complete the following table : (MARCH-2010)
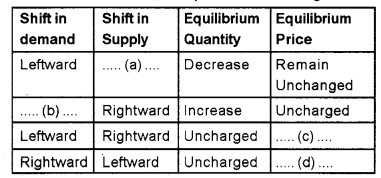
Answer:
a) Leftward
b) Rightward
c) Decrease
d) Increase
Question 4.
Under fixed price analysis of a product market, if quantity supplied is either in excess or falls short of quantity demanded price will change because of excess supply or demand. In this occasion (MARCH-2010)
a) How the equilibrium is determined?
b) Name the principle.
Answer:
a) Assume that the elasticity of supply is infinite that is the supply schedule is horizontal. In this situation the equilibrium output will be solemnly determined by aggregate amount of demand at this price in the economy.
b) Keynesian analysis or effective demand Principle.
Question 5.
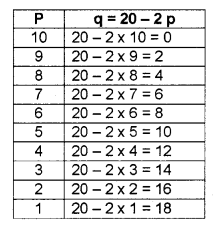
The demand function of a monopoly firm is given as q = 20 – 2P, substitute the values of P from 10 to 1. (MAY-2010)
a) Calculate the demand schedule of the commodity.
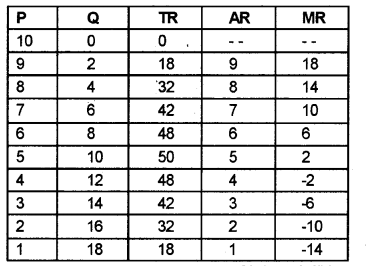
b) From the table calculate the TR, AR and MR values in a tabular form.
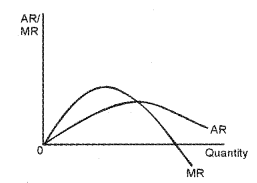
c) Draw the AR and MR curve in same set of axis.
d) When the price elasticity is more than one?
Answer:
a)
b)
c)
d) Price elasticity is more than one when MR is positive.
Question 6.
Find the correct term for the following : (MAY-2010)
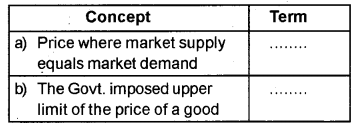
Answer:
a) Equilibrium price
b) Price ceiling
Question 7.
The Government imposed lower limit on the price that may charged for a particular good is called price floor. Give two examples for imposition of price floor. The Government imposed lower limit on the price that may charged for a particular good is called price floor. Give two examples for imposition of price floor (MAY-2010)
Answer:
i) Price floor fixed for paddy
ii) Price floor fixed for food grains
Question 8.
This is a demand curve for a branded umbrella. (MARCH-2011)
a) If the demand for umbrella increases during rainy season, what term we use in economics to denote this change? Draw the curve.
b) What you call this change when the price of umbrella increased, the demand decreased.
Answer:
a) Rightward shift or increase in demand
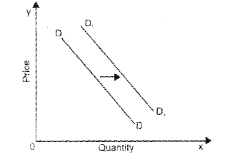
b) Upward movement along the same demand curve or there is contraction of demand.
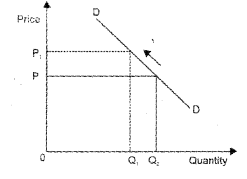
Question 9.
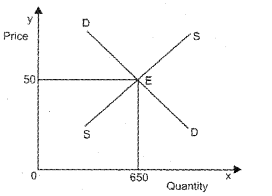
The demand and supply equations of a commodity in a perfectly competitive market are given as qd = 700 – P qs = 500 + 3P (MARCH-2011)
Calculate:
a) Equilibrium price
b) Equilibrium quantity
c) Based on the given supply and demand equations draw equilibrium situation on a diagram.
Answer:
a) Equilibrium price

b) Equilibrium quantity
qd = 700 – P
= 700 – 50
= 650
c)
Question 10.
Imposition of the price ceiling below the equilibrium price leads to (MARCH-2012)
a) Excess demand
b) Excess supply
c) Deficit demand
d) Deficit supply
Answer:
a) Excess demand
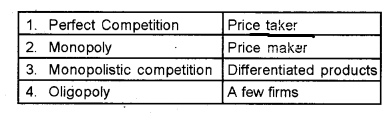
Question 11.
Match the following: (MARCH-2012)
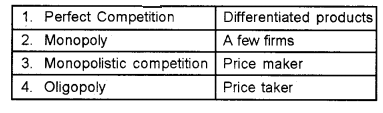
Answer:
Question 12.
Welfare considerations enable the govt, to impose price floor for some goods and services. Mention any one example of imposition of price floor. (MARCH-2013)
Answer:
In India, floor prices are fixed for a variety of commodities like paddy, rubber, wheat, coconut etc.
Question 13.
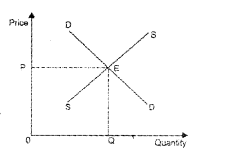
The following diagram shows equilibrium market price determined by the equality between demand and supply. (MARCH-2013)
Show the effect of change in demand and supply on equilibrium price and output under the following situations (use diagrams)
i) Increase in demand or when the demand curve shift rightwards.
ii) Increase in supply or when supply curve shift rightwards.
Answer:
i) When demand curve shifts to right (increase in demand), there will be increase in equilibrium price and increase in equilibrium quantity. This change is shown in the diagram.
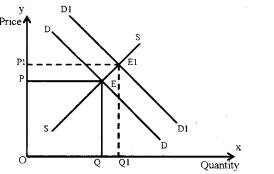
ii) When supply curve shifts to right (increase in supply), the equilibrium price decreases and the equilibrium quantity increases. This is given in the following diagram.
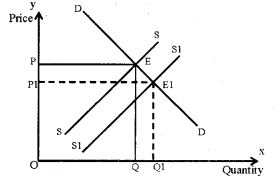
Question 14.
Diagrammatically illustrate the impact of (MAY-2014)
a) Price ceiling and
b) Price floor on market equilibrium
Answer:
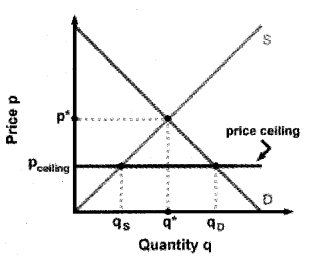
a) Price Ceilings
A price ceiling occurs when the government puts a legal limit on how high the price of a product can be. In order for a price ceiling to be effective, it must be set below the natural market equilibrium.
When a price ceiling is set, a shortage occurs. For the price that the ceiling is set at, there is more demand than there is at the equilibrium price. There is also less supply than there is at the equilibrium price, thus there is more quantity demanded than quantity supplied. An inefficiency occurs since at the price ceiling quantity supplied the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost. This inefficiency is equal to the dead weight welfare loss.
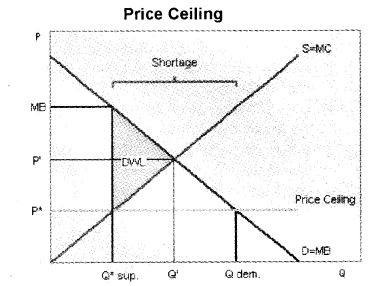
This graph shows a price ceiling. P* shows the legal price the government has set, but MB shows the price the marginal consumer is willing to pay at Q*, which is the quantity that the industry is willing to supply. Since MB > P* (MC), a dead weight welfare loss results. P’ and Q’ show the equilibrium price. At P* the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied. This is what causes the shortage,
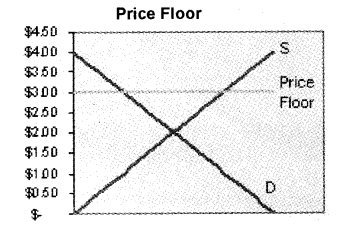
b) Price Floors
A price floor is the lowest legal price a commodity can be sold at. Price floors are used by the government to prevent prices from being too low. The most common price floor is the minimum wage the minimum price that can be payed for labor. Price floors are also used often in agriculture to try to protect farmers.
Question 15.
From the list of goods given below, find out the one which cannot be provided through market mechanism? (MARCH-2015)
a) Private goods
b) Public goods
c) Merit goods
d) Club goods
Answer:
b) Public goods
Question 16.
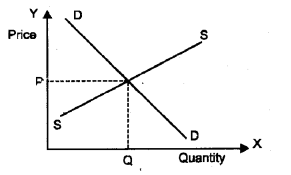
The following diagram shows the equilibrium price of wheat determined by the supply curve ‘SS’ and market demand curve ‘DD’. With the help of the diagram answer the questions given below. (MARCH-2015)
a) If the Government imposes price ceiling on wheat, what happens to the demand for wheat?
b) Define price ceiling.
c) Write down two adverse impacts of price ceiling on the consumers.
Answer:
Question 17.
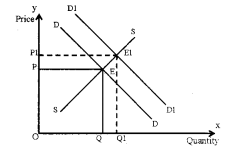
Explain through a diagram the effect of a rightward shift (increase) of both the demand and supply curves on the equilibrium price and quantity? (MAY-2015)
Answer:
When demand curve shifts to right (increase in demand), there will be increase in equilibrium price and increase in equilibrium quantity. This change is shown in the diagram.
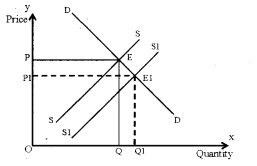
When supply curve shifts to right (increase in supply), the equilibrium price decreases and the equilibrium quantity increases. This is given in the following diagram.
Question 18.
List the 3 different ways in which an oligopoly firm may behave. (MARCH-2016)
Answer:
If the market of a particular commodity consists of more than one seller but the number of sellers is few, the market structure is termed oligopoly. The special case of oligopoly where there are exactly two sellers is termed duopoly. We shall explain the different ways in which the oligopoly firms may behave.
Firstly duopoly firms may collude together and decide not to compete with each other and maximize total profits of the two firms together. In such a case the two firms would behave like a single monopoly firm that has two different factories producing the commodity.
Secondly, take the case of a duopoly where each of the two firms decide how much quantity to produce by maximizing its own profit assuming that the other firm would not change the quantity that it is supplying. We can examine the impact using a simple example where both the firms have zero cost.
Thirdly, some economists argue that oligopoly market structure makes the market price of the commodity rigid, i.e., the market price does not move freely in response to changes in demand.
Question 19.
Explain the consequence if price prevailing in the market is fixed: (MARCH-2016)
i) Above the equilibrium price (Price floor)
ii) Below the equilibrium price (Price ceiling)
Answer:
i) Excess supply
ii) Excess demand
Question 20.
Demand and supply equations of commodity X is given by (MARCH-2016)
qd = 100- P
qs = 70 + 2P
find the equilibrium price and quantity.
Answer:

Question 21.
Imposition of price floor leads to (MAY-2016)
a) an excess demand
b) an excess supply
c) normal demand
d) any of the above
Answer:
b) an excess supply
Question 22.
State whether the following statements are true or false: (MAY-2016)
a) With supply curve remaining unchanged, when demand curve shifts rightward, the equilibrium quantity decreases and equilibrium price decreases.
b) In a perfectly competitive market, equilibrium occurs where market demand equals market supply.
Answer:
a) False
b) True
Question 23.
Suppose onion price increases above ₹100 per kg and the government imposes price ceiling. (MAY-2016)
a) What is price ceiling?
b) What are the consequence of imposing price ceiling?
Answer:
a) Price ceiling mean maximum price. It is the maximum price fixed by the government. The aim of price ceiling is to protect consumers. Government fixes price ceiling for essential products and medicines to protect the interests of the consumers.
Consequence of imposing price ceiling:
1. Black marketing
2. Malpractices by fair price shops
3. Sale of inferior quality goods.
Question 24.
Suppose the demand and supply functions of wheat are given by QD = 800 – 4P and QS= 600 + 4P respectively.
i) Find the equilibrium price and quantity demanded. (MARCH-2017)
ii) Due to a shortage of fertilizers, the cost of production of wheat is increased. So that the new supply function is
QS = 400 + 4P. What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity demanded?
Answer:
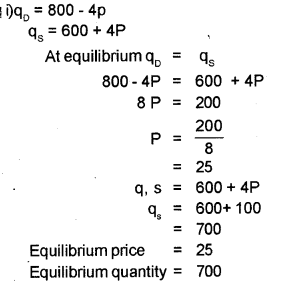

The equilibrium price will increase and equilibrium quantity will fall.
Question 25.
How does equilibrium price and quantity demand affect when (MARCH-2017)
i) Both demand and supply curves shift in the same direction.
ii) Demand and supply curves shift in the opposite directions.
Answer:
i) Both demand and supply curve shift in the same direction.
When the demand curve and supply curve shift to right: For a given price, more quantity is demanded as well as more quantity is supplied. The demand curve and supply curve shifted to right to show a greater quantity for a given price. If supply increases relatively greater than the equilibrium price is smaller, but if demand increases relatively greater than the intersection is higher and the price obtained will be higher. Only than it is certain that there will be more quantity at new equilibrium price.
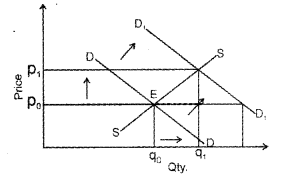
When the demand curve and supply curve shifts to left: The price may increase or decrease depending whether supply decreases relatively more or demand decrease relatively more, respectively, and the only certainty is that there is less quantity at new equilibrium point
ii) Demand curve shifts left and supply curve shifts right: Demand decreases and supply increases. The price was fallen, but if supply curve shifts a lot more right than the demand curve shifts left, then the new equilibrium point will mean more quantity is supplied at a much lower price.
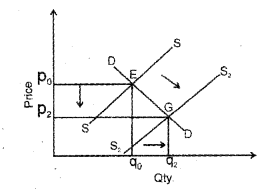
Demand curve shifts right and supply curve shift left: Demand increases and supply decreases. The price will increase but depending on how far the supply curve shifts left, the equilibrium quantity would be more or less or same. This shift will see a higher equilibrium point with less quantity demand.