Kerala Plus One Accountancy Notes Chapter 6 Depreciation, Provisions and Reserves
Summary:
Meaning of depreciation:
Depreciation is decline in the value of a tangible fixed asset. In accounting depreciation is the process of allocating depreciable cost over useful life of a fixed asset.
Depreciation and similar terms:
Depreciation term is used in the context of tangible fixed assets. Depletion (in the context of extractive industries), and amortisation (in the context of intangible assets) are other related terms.
Factors Affecting Depreciation:
- Wear and Tear due to use and/or passage of time
- Expiration of Legal Rights
- Obsolescence
Importance of depreciation:
- Depreciation must be charged to ascertain true and fair profit or loss.
- Depreciation is a non-cash operating expense.
Methods of charging depreciation:
Depreciation amount can be calculated using:
- Straight line method, or
- Written down value method
Methods of recording depreciation:
In the books of account there are two types of arrangements for recording depreciation on fixed assets.
- Charging depreciation to asset account or
- Creating provision for depreciation/ accumulated depreciation account.
Charging depreciation to asset account:
According to this arrangement depreciation is deducted from the depreciable cost of the asset (credited to the asset account) and charged (or debited) to profit and loss account. Journal entries under this recording method are as follows:

2. Following two entries are recorded at the end of every year.
(a) For deducting depreciation amount from the cost of the asset.

(b) For charging depreciation to profit and loss account

3. Balance Sheet Treatment
When this method is used, the fixed asset appears at its net book value (ie. cost less depreciation charged till date) on the asset side of the balance sheet and not at its original cost (also known as historical cost).
Creating Provision for depreciation account/ Accumulated depreciation Account:
This method is designed to accumulate the depreciation provided on an asset in a separate account generally called “Provision for Depreciation” or “Accumulated Depreciation” account.
The following journal entries are recorded under this method:

2. The following two journal entries are recorded at the end of each year
(a) For crediting depreciation amount to provision for depreciation account.

(b) For charging depreciation to profit and loss account
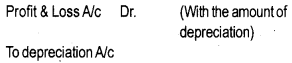
3. Balance Sheet treatment
In the balance sheet the fixed asset continues to appear at its original cost on the asset side. The depreciation charged till that date appears in the provision for depreciation account, which is shown either on the “liabilities side” of the balance sheet or by way of deduction from the original cost of the asset concerned on the asset side of the balance sheet.
Disposal of Asset:
Disposal of asset can take place either
- At the end of its useful life or
- During the useful life (due to absolescence or any other abnormal factors). In this case the following journal entries are recorded.
1. For the sale of asset as scrap
![]()
2. For transfer of balance in asset account

In case, however “the provision for depreciation account” has been in use for recording the depreciation, then before passing the above entries transfer the balance of the provision for depreciation account to the asset account by recording the following journal entry.
![]()
Factors affecting the amount of depreciation:
- Depreciation amount is determined by Original cost
- Salvage value, and
- Useful life of the asset
Provisions and Reserves:
A provision is a charge against profit. It is created for a known current liability the amount of which is uncertain. Reserve on the other hand, is an appropriation of profit. It is created to strengthen the financial position of the business.
Types of Reserves:
Reserves may be:
- General reserve and specific reserve;
- Revenue reserve and capital reserve.
Secret Reserve:
When the total depreciation charged is higher than the total depreciable cost, the Secret reserve is created. The secret reserve is not explicitly shown in the balance sheet.