Is Malaria an Infectious or Noninfectious Disease
Types of Diseases :
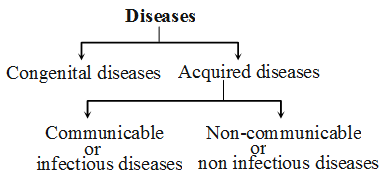
Human diseases are broadly grouped into two categories –
- Congenital Diseases :
These diseases are those which are present since birth. - Acquired Diseases :
These diseases are those which develop after birth.
Acquired Diseases :
Acquired diseases can be broadly classified into two types –
- Communicable
- Non-communicable
1. Infectious (communicable) Diseases :
These diseases are spread from infected person to other in various ways, i.e., through air, water, food, physical contact, sexual act and insects. The causative agents of these diseases are called pathogens or infectious agents. These may be viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoans (single-called animals) and different kinds of worms (multicellular organisms). Common diseases caused by these infectious agents are mentioned in Table.
Infectious Agents | Diseases |
I. Viruses | 1. Common cold 2. Influenza 3. Dengue fever 4. Poliomyelitis 5. Hepatitis-B 6. AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrom 7. Chicken pox 8. Measles 9. Mumps 10. SARS 11. Swine Flu (H1N1) |
| II. Bacteria | 1. Typhoid fever 2. Cholera 3. Tuberculosis 4. Anthrax 5. Tetanus 6. Food poisoning |
III. Fungi | 1. Many common skin infectious (e.g., ring worm, athlete’s foot) |
IV. Protozoans | 1. Malaria 2. Kala-azar 3. Amoebic dysentry 4. Sleeping sickness |
| V. Worms | 1. Intestinal worm infections (taeniasis by tape worm and ascariasis by round worm). 2. Elephantiasis |
2. Non-Infectious (non-communicable) Diseases :
These diseases remain confined to the person who develops them and do not spread to other. Non-infectious diseases may occur due to :
- Malfunctioning of some important body organs (e.g., heart diseases, epilepsy etc.);
- Inadequate diet or deficiency of nutrients, minerals and vitamins (e.g., Kwashiorkor, marasmus, beriberi, scurvy, night blindness etc.
- Hypo or hyper secretion of hormones (e.g. diabetes, iodine-deficiency goiter, critinism, myxodema, exopthalmic goitre etc.
- Malfunctioning of immune system (e.g., allergy)
- Cancer.