Hyperbola
A hyperbola is the locus of a point in a plane which moves in the plane in such a way that the ratio of its distance from a fixed point in the same plane to its distance from a fixed line is always constant which is always greater than unity.
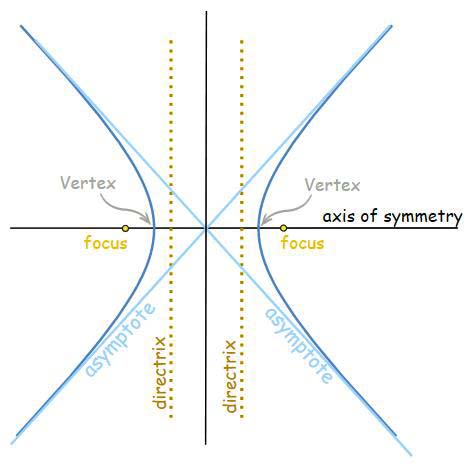
Standard equation of the hyperbola
Let S be the focus, ZM be the directrix and e be the eccentricity of the hyperbola, then by definition, 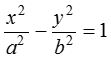 , where b2 = a2(e2 − 1).
, where b2 = a2(e2 − 1).
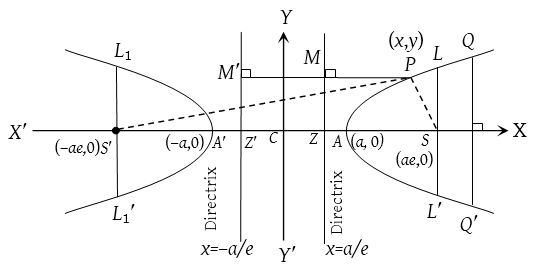
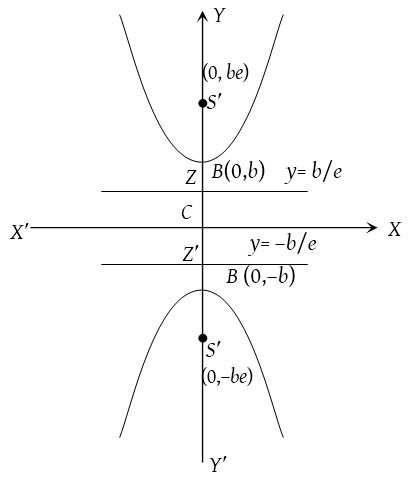
Conjugate hyperbola
The hyperbola whose transverse and conjugate axis are respectively the conjugate and transverse axis of a given hyperbola is called conjugate hyperbola of the given hyperbola.
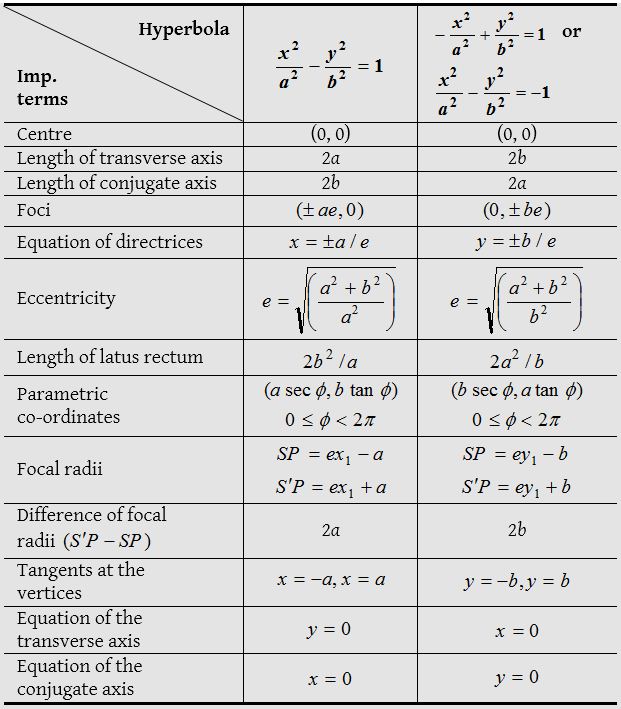
 Difference between both hyperbolas will be clear from the following table:
Difference between both hyperbolas will be clear from the following table:
Special form of hyperbola
If the centre of hyperbola is (h, k) and axes are parallel to the co-ordinate axes, then its equation is 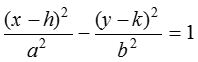 .
.
Auxiliary circle of hyperbola
Let 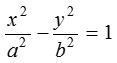 be the hyperbola, then equation of the auxiliary circle is x2 + y2 = a2.
be the hyperbola, then equation of the auxiliary circle is x2 + y2 = a2.
Let ∠QCN = ϕ. Here P and Q are the corresponding points on the hyperbola and the auxiliary circle (0 ≤ ϕ < 2π).
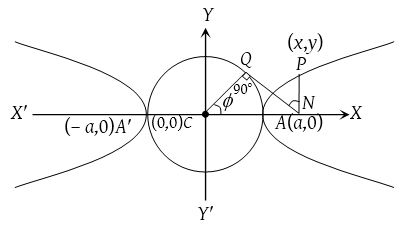
Parametric equations of hyperbola
The equations x = a sec ϕ and y = b tan ϕ are known as the parametric equations of the hyperbola 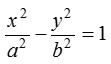 .
.
This (a sec ϕ, b tan ϕ) lies on the hyperbola for all values of ϕ.
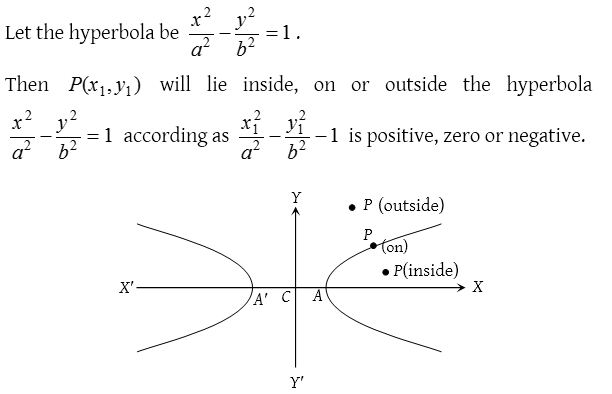
Position of a point with respect to a hyperbola
Intersection of a line and a hyperbola

Equations of tangent in different forms

