Derivative Rules
The rate of change of one quantity with respect to some another quantity has a great importance.
The rate of change of a quantity ‘y’ with respect to another quantity ‘x’ is called the derivative or differential coefficient of y with respect to x.
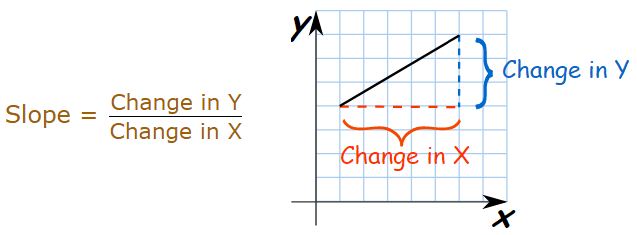
The Derivative means the slope of a function at any point.
Some Standard Differentiation Formulae
(1) Differentiation of some common functions:
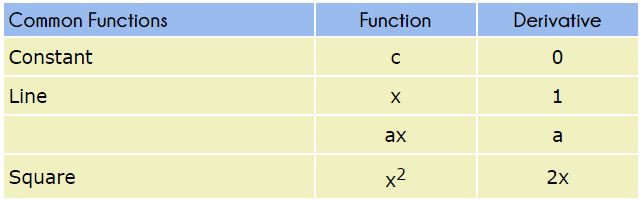
(2) Differentiation of algebraic functions:
In particular
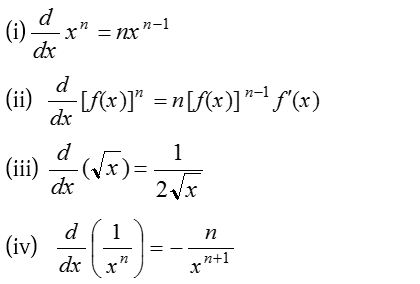
(3) Differentiation of trigonometric functions:
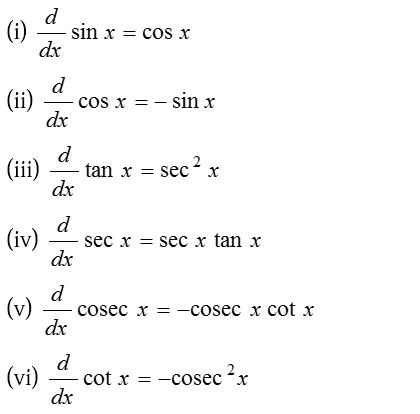
(4) Differentiation of logarithmic and exponential functions:
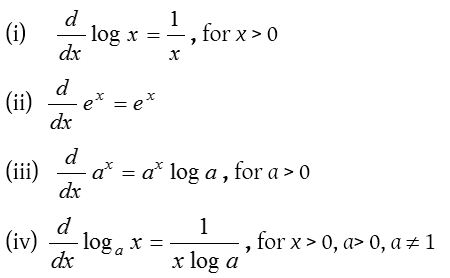
(5) Differentiation of inverse trigonometrical functions:
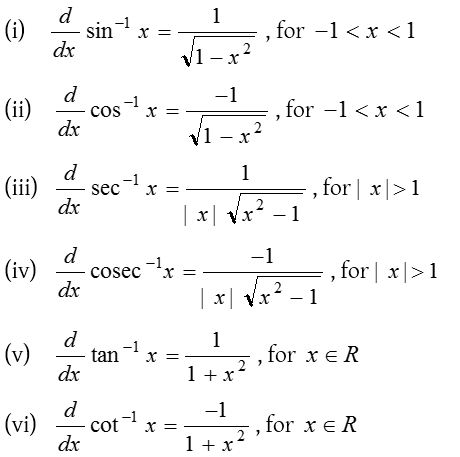
(6) Differentiation of hyperbolic functions:
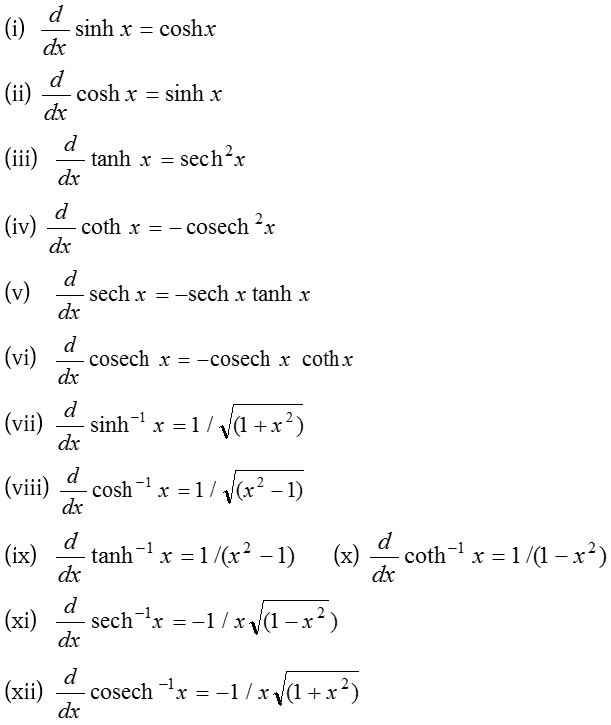
(7) Suitable substitutions
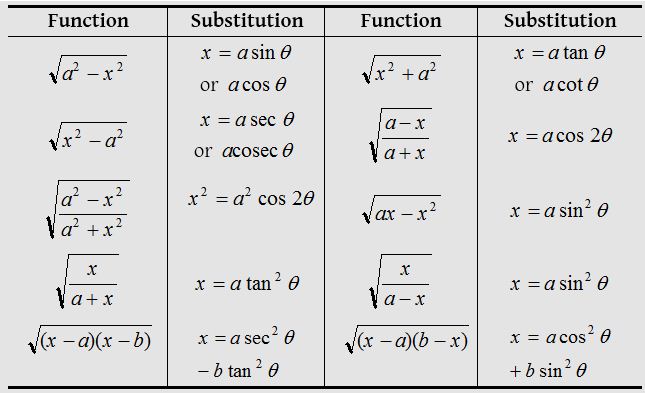
Rules for Differentiation
Let f(x), g(x) and u(x) be differentiable functions
- If at all points of a certain interval, f'(x) = o, then the function f(x) has a constant value within this interval.
- Chain rule
(i) Case I: if y is a function of u and u is a function of x, then derivative of y with respect to x is
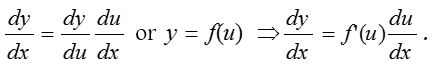
(ii) Case II: If y and x both are expressed in terms of t, y and x both are differentiable with respect to t, then
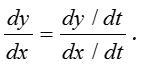
- Sum and difference rule: Using linear property
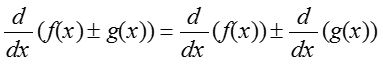
- Product rule
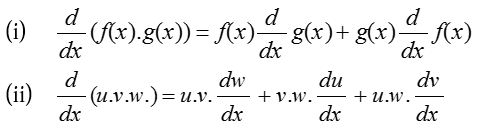
- Scalar multiple rule:
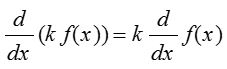
- Quotient rule:
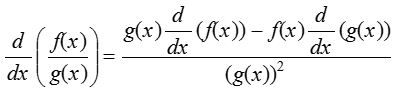
Provided g≠0.
