Trigonometric Ratios Of Complementary Angles
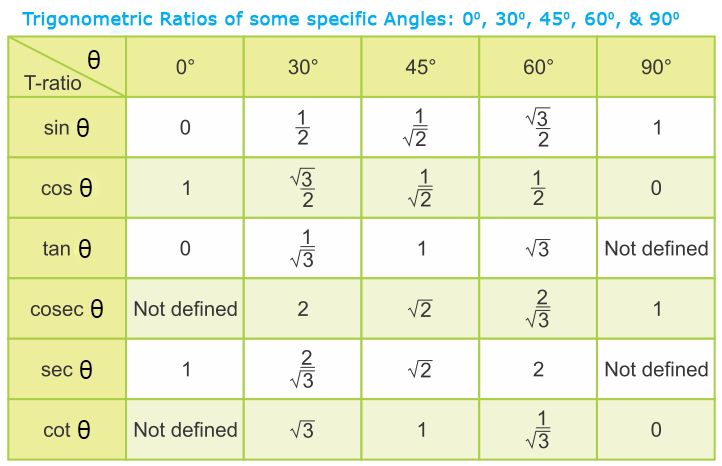


We know Trigonometric ratios of complementary angles are pair of angles whose sum is 90°
Like 40°, 50°, 60°, 30°, 20°, 70°, 15°, 75° ; etc,
Formulae:
sin (90° – θ) = cos θ, cot (90° – θ) = tanθ
cos (90° – θ) = sin θ, sec (90° – θ) = cosec θ
tan (90° – θ) = cot θ, cosec (90° – θ) = sec θ
Trigonometric Ratios Of Complementary Angles With Examples
Example 1: \( \text{Evaluate }\frac{\tan 65{}^\circ }{\cot 25{}^\circ }. \)
Sol. ∵ 65° + 25° = 90°
\( \frac{\tan 65{}^\circ }{\cot 25{}^\circ }=\frac{\tan \,(90{}^\circ -25{}^\circ )}{\cot \,25{}^\circ }=\frac{\cot 25{}^\circ }{\cot 25{}^\circ }=1 \)
Example 2: Without using trigonometric tables, evaluate the following:
\(\left( i \right)~\text{ }\frac{\cos \,\,37{}^\text{o}}{\sin \,\,53{}^\text{o}}\text{ }\left( ii \right)~\frac{\sin \,\,41{}^\text{o}}{\cos \,\,49{}^\text{o}}~\text{ }\left( iii \right)~\frac{\sin \,\,30{}^\text{o}17\acute{\ }}{\cos \,\,59{}^\text{o}\,43\acute{\ }}\)
Sol. (i) We have,
\( \frac{\cos \,\,37{}^\text{o}}{\sin \,\,53{}^\text{o}}=\frac{\cos (90{}^\text{o}-53{}^\text{o})}{\sin \,\,53{}^\text{o}}=\frac{\sin \,\,53{}^\text{o}}{\sin \,\,53{}^\text{o}}=1 \)
[∵ cos(90º – θ) = sin θ]
(ii) We have,
\( \frac{\sin \,\,41{}^\text{o}}{\cos \,\,49{}^\text{o}}=\frac{\sin (90{}^\text{o}-49{}^\text{o})}{\cos \,49{}^\text{o}}=\frac{\cos \,49{}^\text{o}}{\cos \,49{}^\text{o}}=1 \)
[∵ sin (90º – θ) = cos θ]
(iii) We have,
\( \frac{\sin \,\,30{}^\text{o}\,17\acute{\ }}{\cos \,\,59{}^\text{o}\,43\acute{\ }}=\frac{\sin (90{}^\text{o}-59{}^\text{o}43\acute{\ })}{\cos \,59{}^\text{o}43\acute{\ }}=\frac{\cos \,59{}^\text{o}43\acute{\ }}{\cos \,59{}^\text{o}43\acute{\ }}=1 \)
Example 3: Without using trigonometric tables evaluate the following:
(i) sin2 25º + sin2 65º (ii) cos2 13º – sin2 77º
Sol. (i) We have,
sin2 25º + sin265º = sin2 (90º – 65º) + sin2 65º
= cos265º + sin265º = 1
[∵ sin (90º – θ) = cos θ]
(ii) We have,
cos213º– sin277º = cos2(90º – 77º) – sin277º
= sin277º – sin277º = 0
[∵ cos (90º – θ) = sin θ]
Example 4: \( (\text{i})\text{ }\frac{\cot \,\,54{}^\text{o}}{\tan \,\,36{}^\text{o}}+\frac{\tan \,\,20{}^\text{o}}{\cot \,\,70{}^\text{o}}-2 \)
(ii) sec 50º sin 40° + cos 40º cosec 50º
Sol. (i) We have,
\( \frac{\cot \,\,54{}^\text{o}}{\tan \,\,36{}^\text{o}}+\frac{\tan \,\,20{}^\text{o}}{\cot \,\,70{}^\text{o}}-2 \)
\( =\frac{\cot (90{}^\text{o}-36{}^\text{o})}{\tan 36{}^\text{o}}+\frac{\tan \,20{}^\text{o}}{\cot (90{}^\text{o}-20{}^\text{o})}-2 \)
\( =\frac{\tan \,\,36{}^\text{o}}{\tan \,\,36{}^\text{o}}+\frac{\tan \,\,20{}^\text{o}}{\tan \,\,20{}^\text{o}}-2\)
= 1 + 1 – 2 = 0
(ii) We have,
sec50º sin40º + cos40º cosec50º
= sec(90º – 40º) sin40º + cos40º cosec(90º – 40º)
= cosec40º sin40º + cos40ºsec40º
\( =\frac{\sin \,\,40{}^\text{o}}{\sin \,\,40{}^\text{o}}+\frac{\cos \,\,40{}^\text{o}}{\cos \,\,40{}^\text{o}}\)
= 1 + 1 = 2
Example 5: Express each of the following in terms of trigonometric ratios of angles between 0º and 45º;
(i) cosec 69º + cot 69º
(ii) sin 81º + tan 81º
(iii) sin 72º + cot 72º
Sol. (i) We have,
cosec 69º + cot 69º
= cosec (90º – 21º) + cot (90º – 21º)
= sec 21º + tan 21º
[∵ cosec (90º – θ) = sec θ and cot (90º –θ) = tan θ]
(ii) We have,
sin 81º + tan 81º
= sin (90º – 9º) + tan (90º – 9º)
= cos 9º + cot 9º
[∵ sin (90º – θ) = cos θ and tan (90º –θ) = cot θ]
(iii) We have,
sin 72º + cot 72º
= sin (90º – 18º) + cot (90º – 18º)
= cos 18º + tan 18º
[∵ sin (90º – 18º) = cos 18º and tan (90º –18º) = cot 18º]
Example :6 Without using trigonometric tables, evaluate the following:
\( \frac{{{\sin }^{2}}20{}^\text{o}+{{\sin }^{2}}70{}^\text{o}}{{{\cos }^{2}}20{}^\text{o}+{{\cos }^{2}}70{}^\text{o}}+\frac{\sin (90{}^\text{o}-\theta )\sin \theta }{\tan \theta }+\frac{\cos (90{}^\text{o}-\theta )\cos \theta }{\cot \theta } \)
Sol. \( \frac{{{\sin }^{2}}20{}^\text{o}+{{\sin }^{2}}70{}^\text{o}}{{{\cos }^{2}}20{}^\text{o}+{{\cos }^{2}}70{}^\text{o}}+\frac{\sin (90{}^\text{o}-\theta )\sin \theta }{\tan \theta }+\frac{\cos (90{}^\text{o}-\theta )\cos \theta }{\cot \theta } \)
\( =\frac{{{\sin }^{2}}20{}^\text{o}+{{\sin }^{2}}(90{}^\text{o}-20{}^\text{o})}{{{\cos }^{2}}20{}^\text{o}+{{\cos }^{2}}(90{}^\text{o}-20{}^\text{o})}+\frac{\sin (90{}^\text{o}-\theta )\sin \theta }{\tan \theta }+\frac{\cos (90{}^\text{o}-\theta )\cos \theta }{\cot \theta } \)
\( =\frac{{{\sin }^{2}}20{}^\text{o}+{{\cos }^{2}}20{}^\text{o}}{{{\cos }^{2}}20{}^\text{o}+{{\sin }^{2}}20{}^\text{o}}+\frac{\cos \theta \sin \theta }{\frac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }}+\frac{\sin \theta \cos \theta }{\frac{\cos \theta }{\sin \theta }} \)
\( \left[ \sin (90{}^\text{o}-\theta )=\cos \theta \,\,\,and\cos (90{}^\text{o}-\theta )\,\,=\,\,\sin \theta \right] \)
= 1 + cos2 θ + sin2 θ = 1 + 1 = 2
Example :7 If tan 2θ = cot (θ + 6º), where 2θ and θ + 6º are acute angles, find the value of θ.
Sol. We have,
tan 2θ = cot (θ + 6º)
⇒ cot(90º – 2θ) = cot (θ + 6º)
⇒ 90º – 2θ = θ + 6º ⇒ 3θ = 84º
⇒ θ = 28º
Example :8 If A, B, C are the interior angles of a triangle ABC, prove that
\( \tan \frac{B+C}{2}=\cot \frac{A}{2} \)
Sol. In ∆ABC, we have
A + B + C = 180º
⇒ B + C = 180º – A
\( \Rightarrow \frac{B+C}{2}=\text{ }90{}^\text{o}-\frac{A}{2} \)
\( \Rightarrow \tan \left( \frac{B+C}{2} \right)=\tan \left( 90{}^\text{o}-\frac{A}{2} \right) \)
\( \Rightarrow \tan \left( \frac{B+C}{2} \right)=\cot \frac{A}{2} \)
Example :9 If tan 2A = cot (A – 18°), where 2A is an acute angle, find the value of A.
Sol. tan 2A = cot (A – 18°)
cot (90° – 2A) = cot (A – 18°)
(∵ cot (90° – θ) = tan θ)
90° – 2A = A – 18°
3A = 108°
A = 36°
Example :10 If tan A = cot B, prove that A + B = 90°.
Sol. ∵ tan A = cot B
tan A = tan (90° – B)
A = 90° – B
A + B = 90°. Proved
Example :11 If A, B and C are interior angles of a triangle ABC, then show that
\( \sin \left( \frac{B+C}{2} \right)=\cos \frac{A}{2} \)
Sol. ∵ A + B + C = 180° (a.s.p. of ∆)
B + C = 180° – A
\(\left( \frac{B+C}{2} \right)=90{}^\circ -\frac{A}{2}\)
\( \sin \left( \frac{B+C}{2} \right)=\sin \left( 90{}^\circ -\frac{A}{2} \right) \)
\( \sin \left( \frac{B+C}{2} \right)=\cos \frac{A}{2} \) Proved.
Example :12 Express sin 67° + cos 75° in terms of trigonometric ratios of angles between 0° and 45°.
Sol. ∵ 23 = 90 – 67 & 15 = 90 – 75
∴ sin 67° + cos 75°
= sin (90 – 23)° + cos (90 – 15)°
= cos 23° + sin 15°.